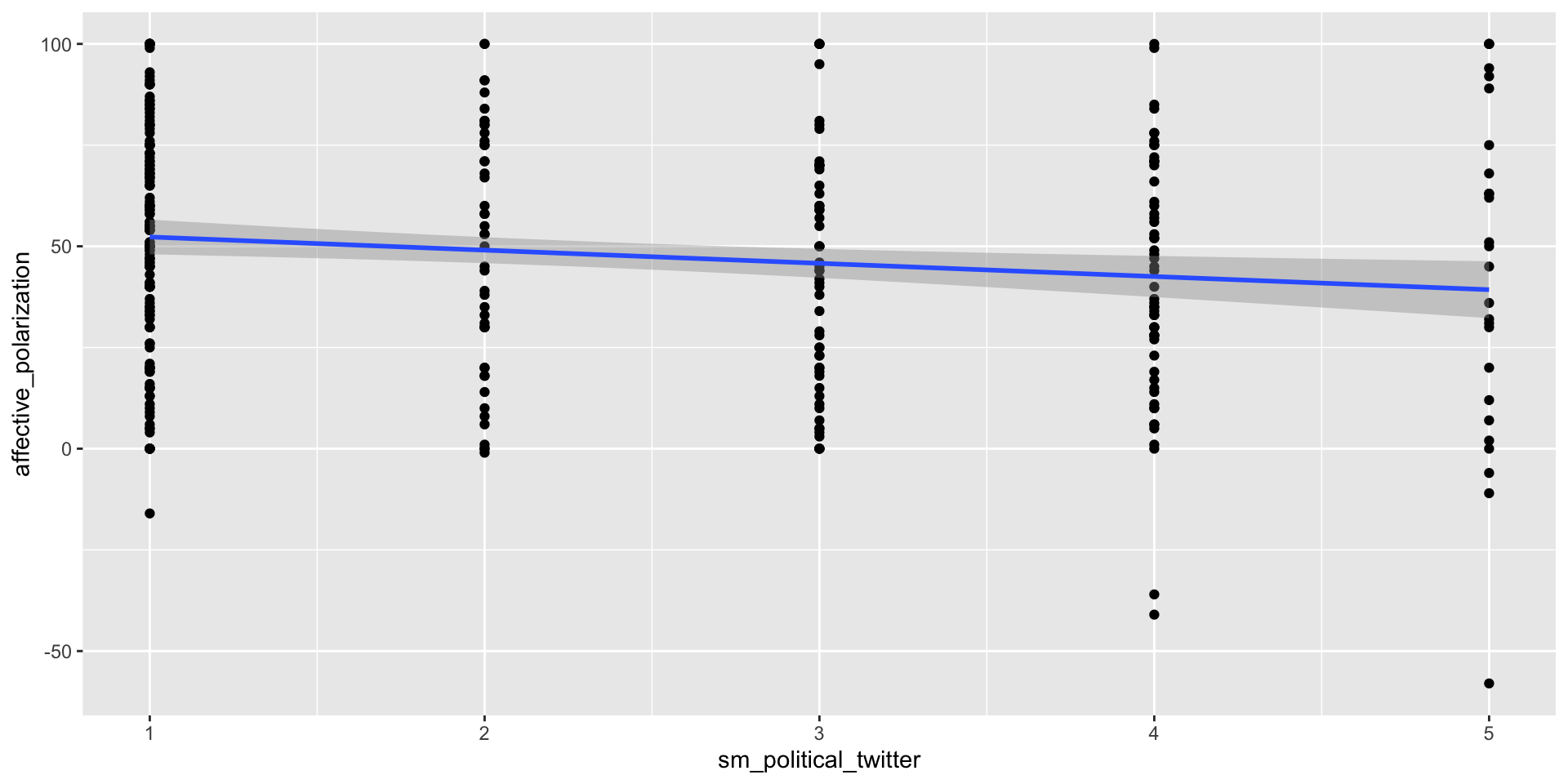
Call:
lm(formula = affective_polarization ~ sm_political_twitter, data = df)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-97.281 -22.303 1.464 22.964 60.719
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 55.559 3.092 17.971 < 2e-16 ***
sm_political_twitter -3.256 1.166 -2.791 0.00554 **
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 29.91 on 345 degrees of freedom
(56 observations deleted due to missingness)
Multiple R-squared: 0.02209, Adjusted R-squared: 0.01925
F-statistic: 7.791 on 1 and 345 DF, p-value: 0.005541POLS 1140
Class Survey
Updated Mar 9, 2025
Monday
Plan
Monday:
Explore initial results from survey
Develop additional questions of the data
Wednesday:
- Finalized results from the data
Friday:
- Last class (Pizza or donuts?)
Attendance Survey!
Click here to take one last attendance survey.
Course Evaluations
Students can access the Course Feedback System through:
Canvas
https://brown.evaluationkit.com
Personalized login link in the reminder emails sent from [email protected].
Group 1
Scott Hilgartner, Harris Laferriere, Tess Naquet-Radiguet, Lily Robinson
Project
Expectations
H1: We expect that as people interact more on social media/ are more active on it, they will have higher degrees of politicization.
H2: We expect that as people engage more with video sharing social media such as Instagram or Tiktok, they will tend to lean more ideologically liberal.
H3: We expect that as people engage more with text sharing social media such as X or Facebook, they will tend to lean more ideologically conservative.
H4: We expect that as people increasingly trust the information they receive on social media, they wil tend to lean more ideologically conservative
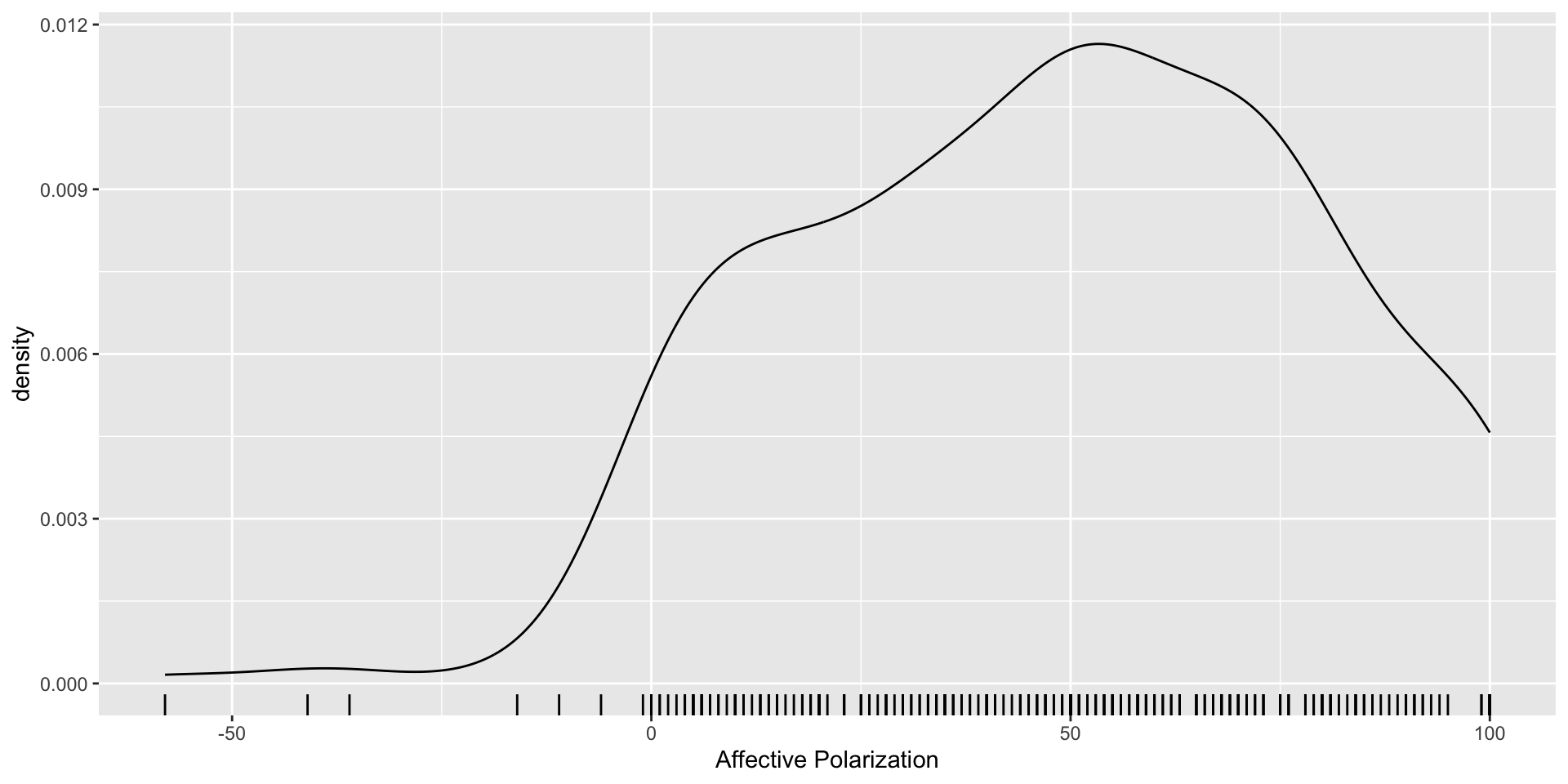
Affective Polarization
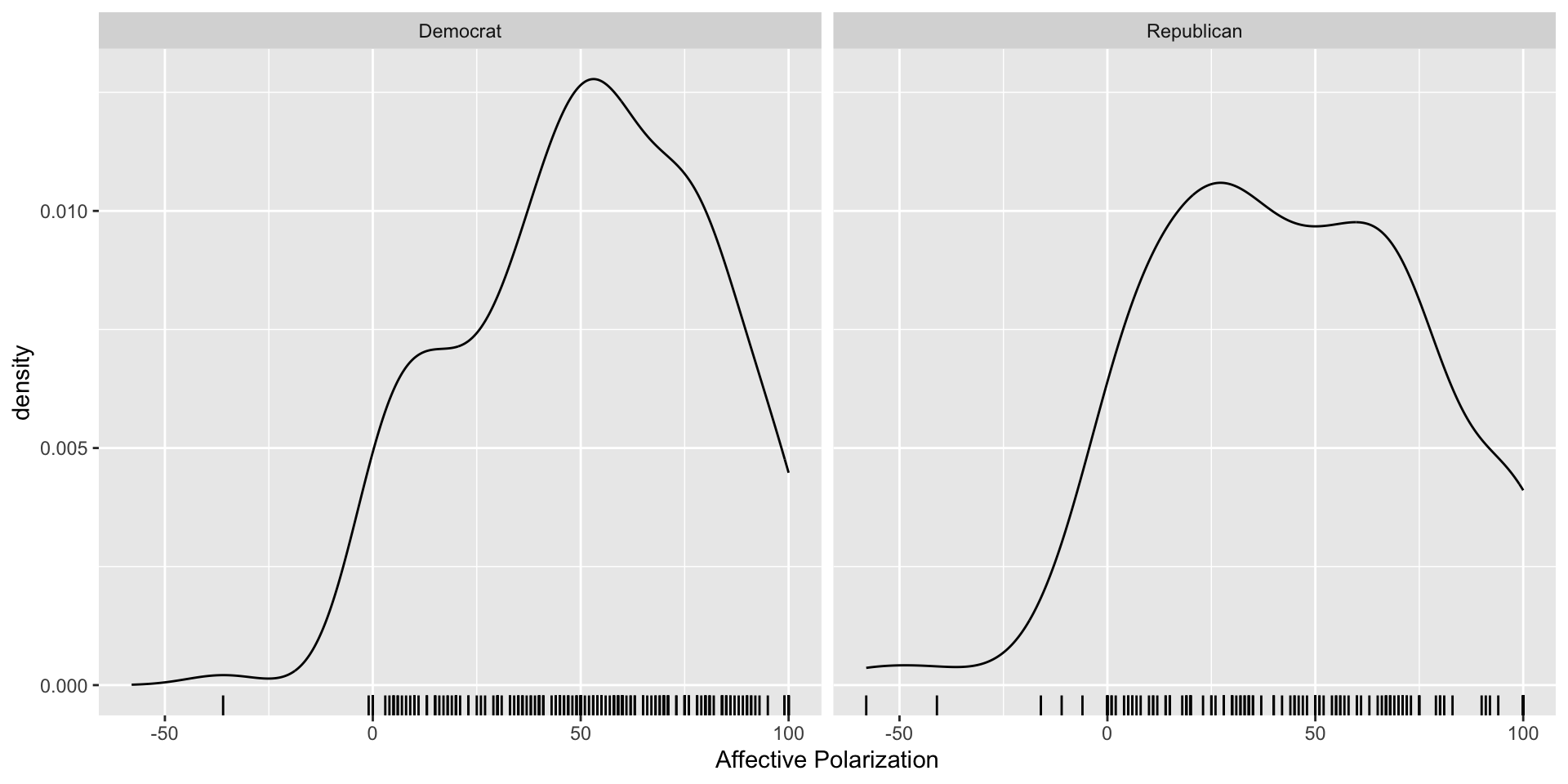
Affective Polarization by Partisanship
Engage with poltical content
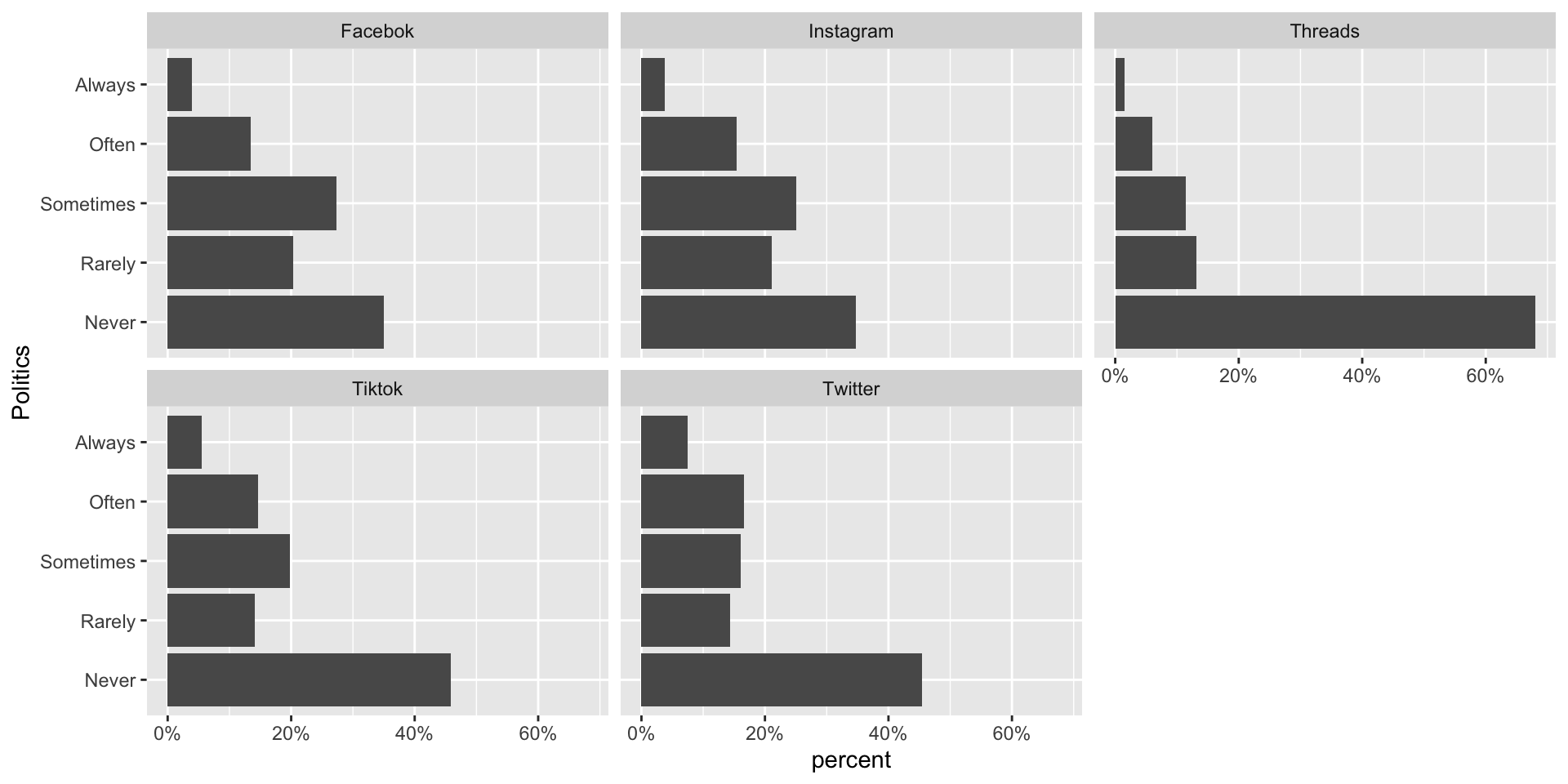
Perceived Ideology
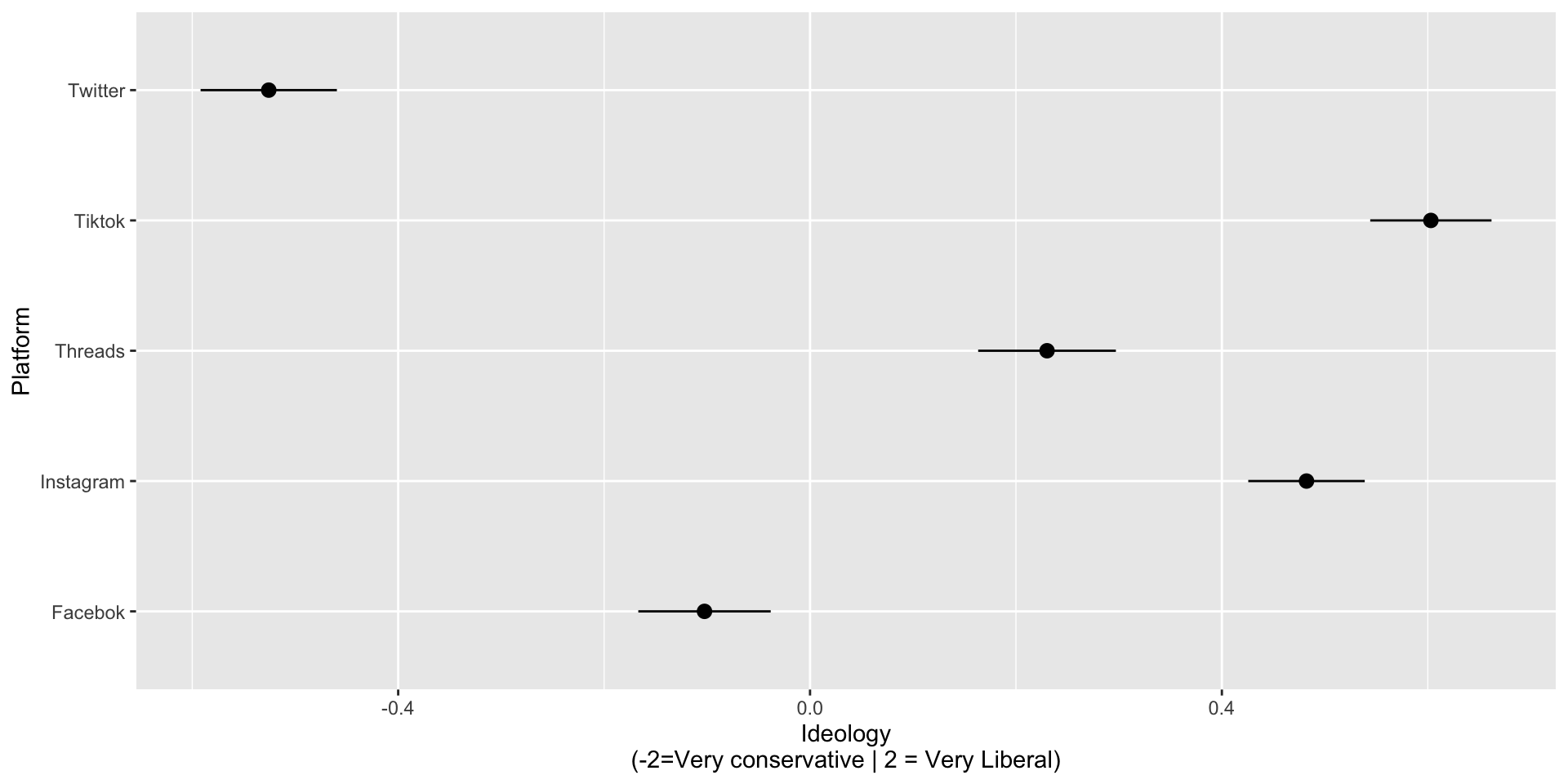
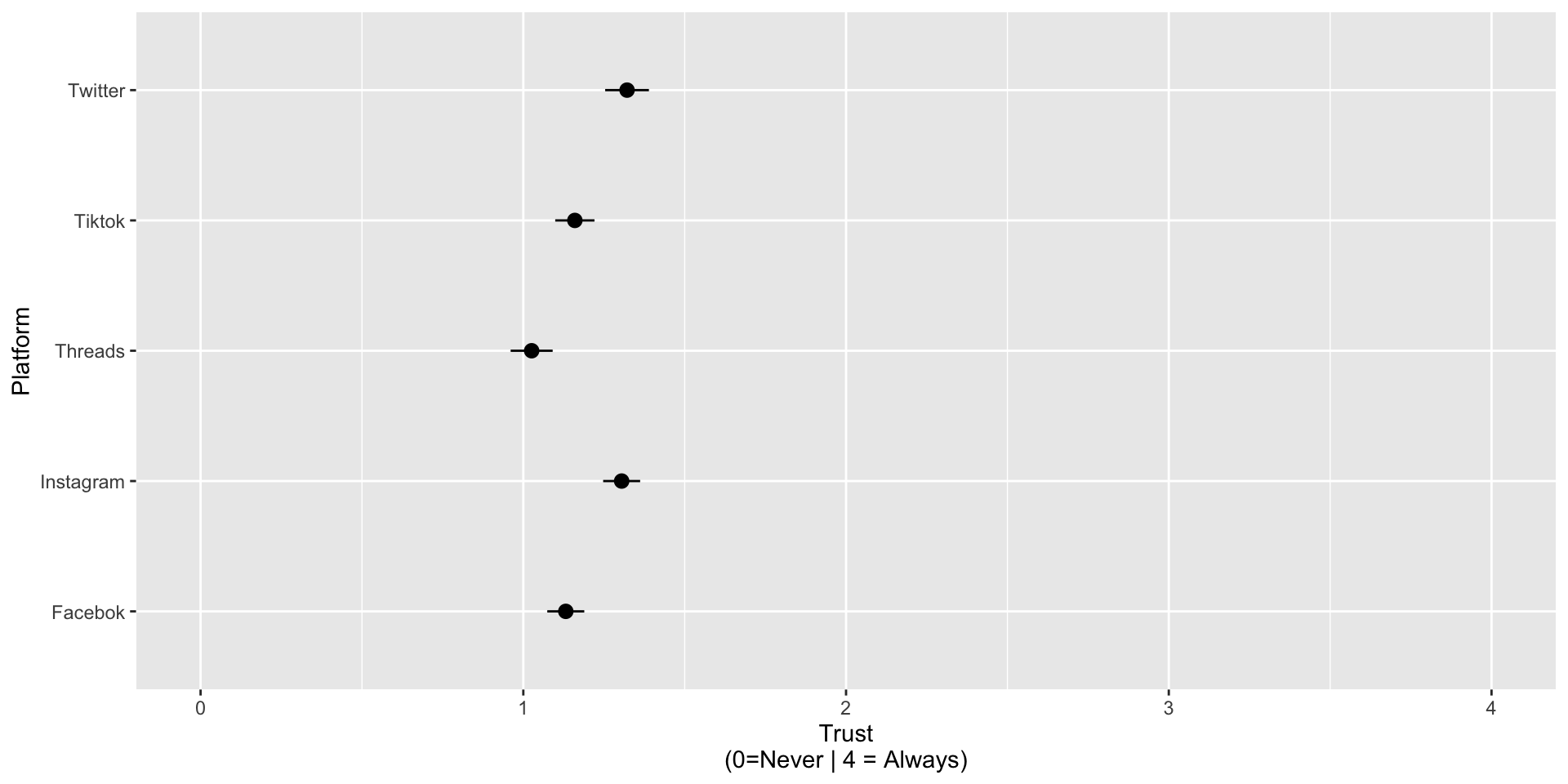
Trust in content by platform
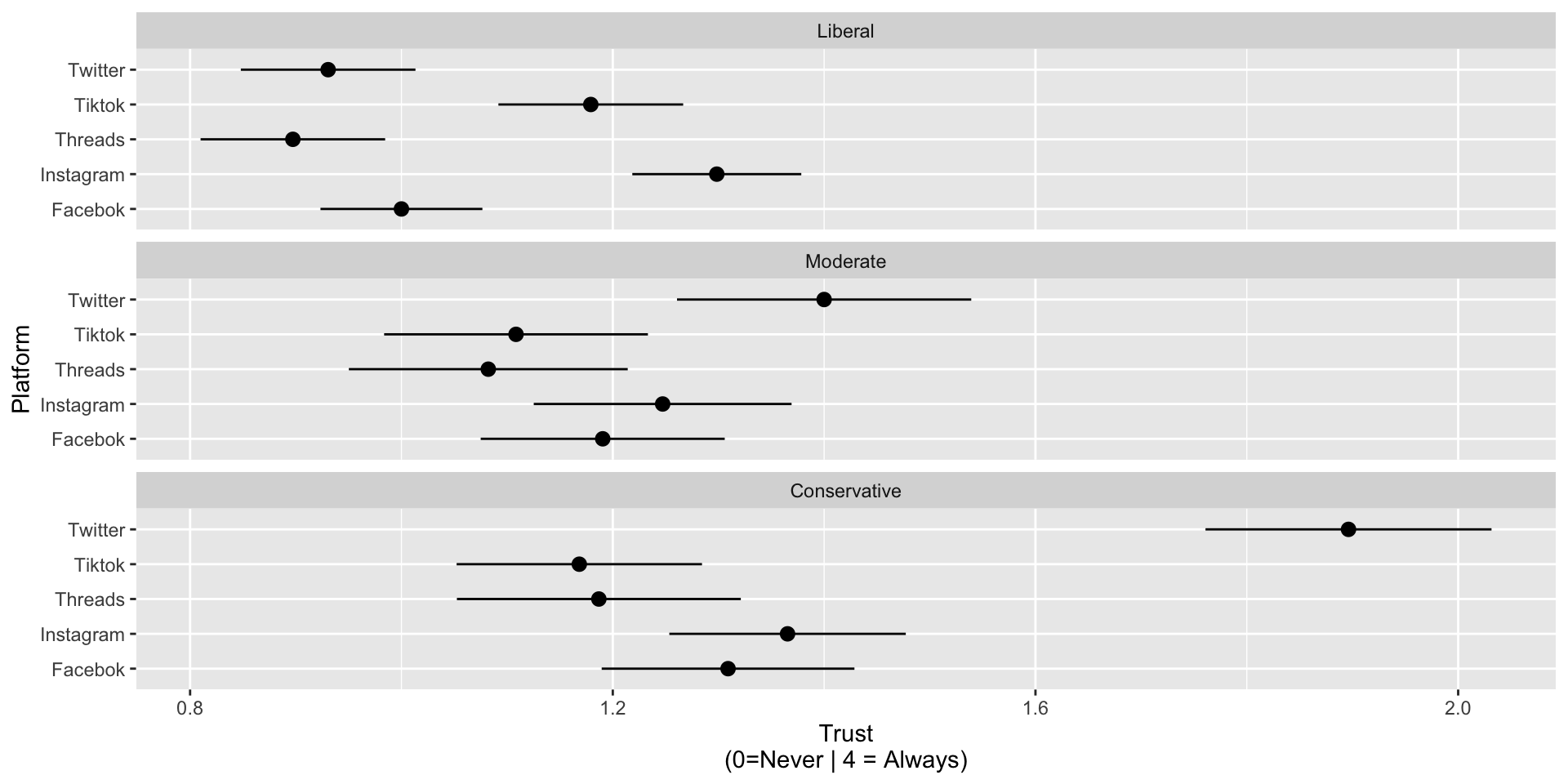
Trust in content by platform and ideolgoy
Media Use and Affective polarization
Group 2
Caleb, Michael, Ruairi, Kate, Cassandra
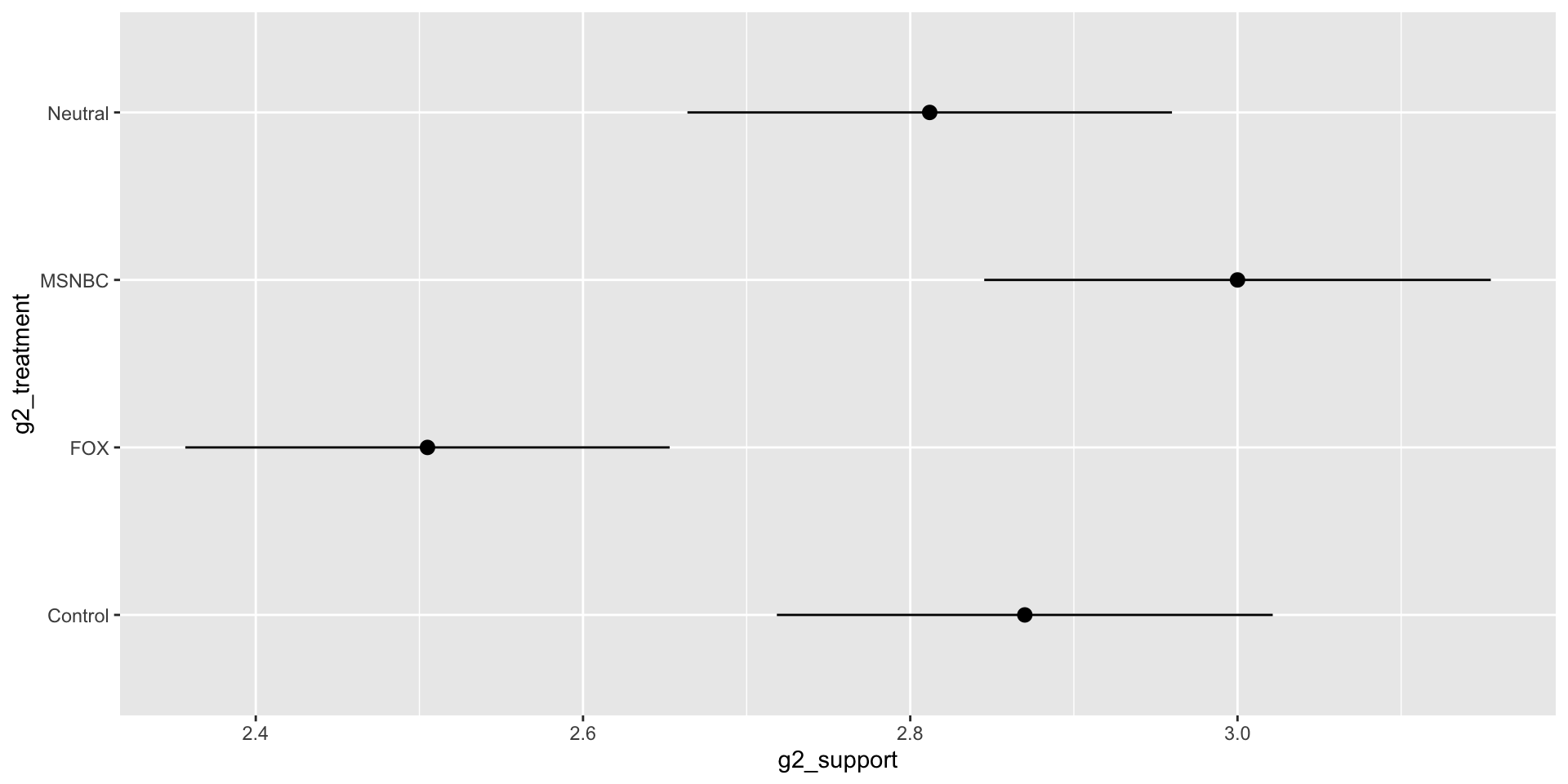
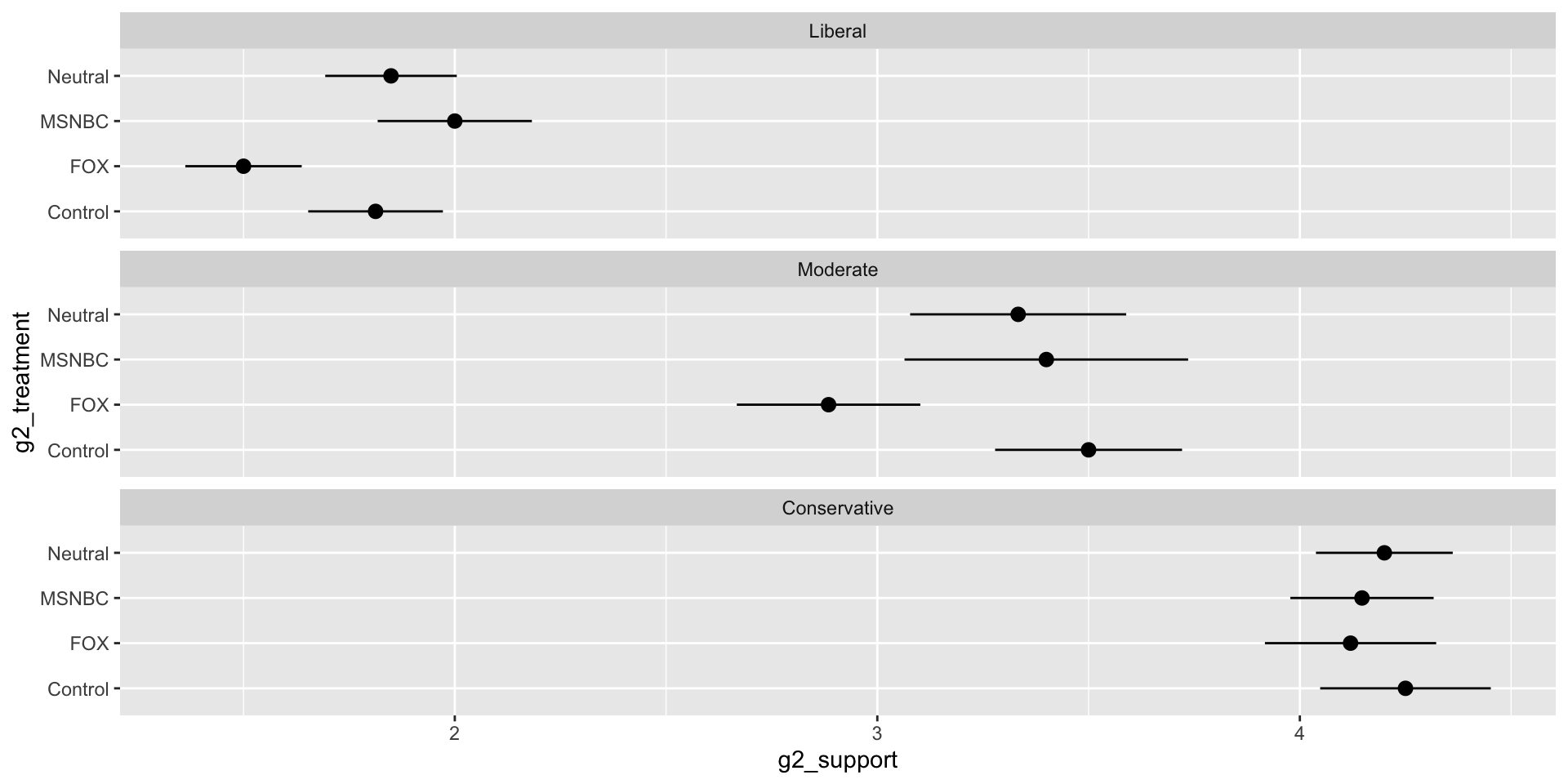
Project
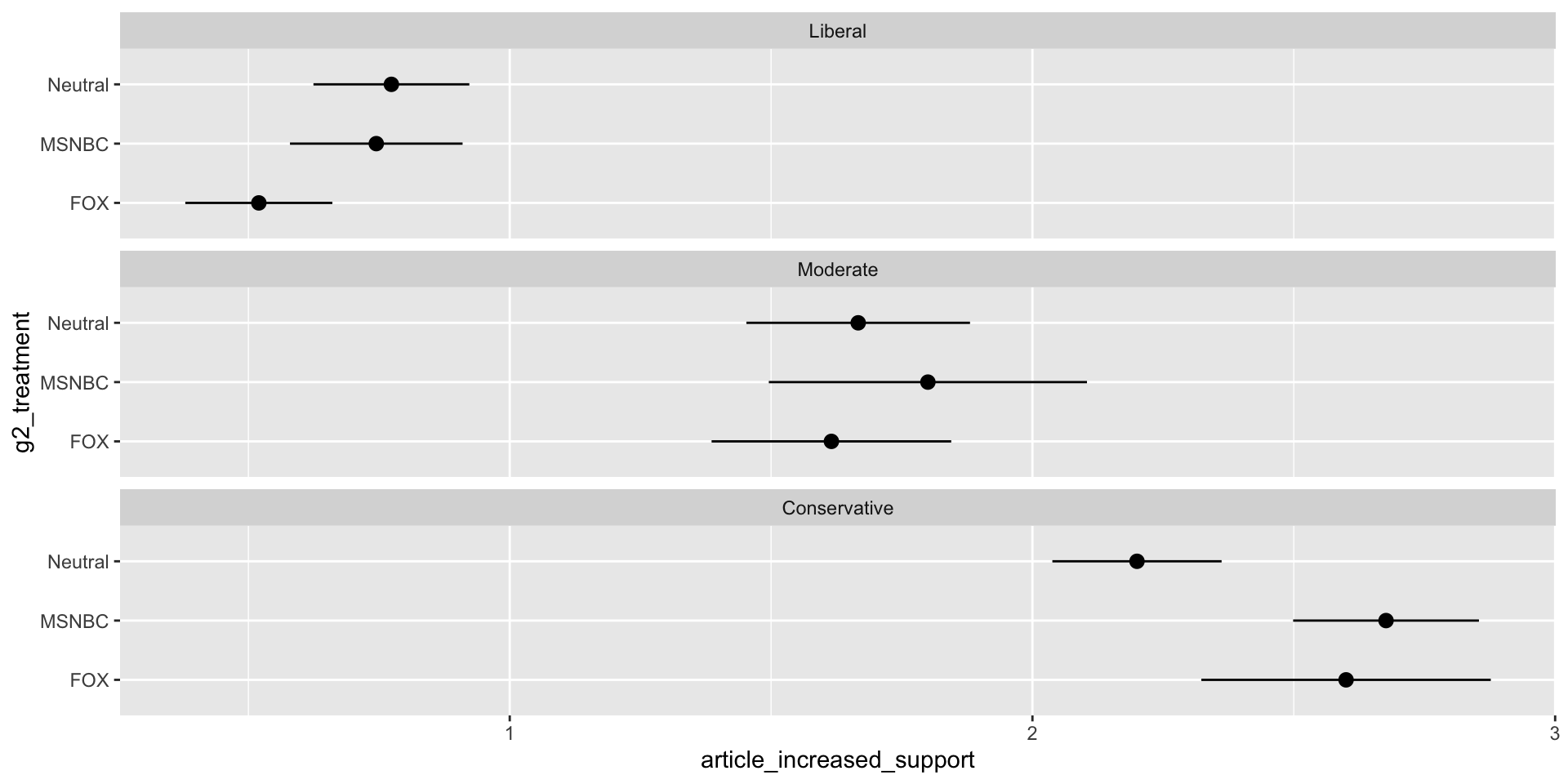
Survey takers will be randomly presented with an article from Fox News, the AP, or MSNBC, all identical in text, and will then be asked a series of questions regarding their opinion on deportations
Expectations
H1: Liberals who read the MSNBC article will be more likely to oppose Trump’s policies than liberals who read neutral articles, and conservatives who read the Fox News article will be more likely to support Trump’s policies.
H2: Liberals who read the Fox News article will also be more likely to oppose Trump’s policies than liberals who read neutral articles, and conservatives who read the MSNBC article will also be more likely to support Trump’s policies.
Results
Group 3
Finn Brown, Lorena Calderon, Mia Hamilton, Ty Pham-Swann
Project
We are interested in evaluating
perceptions of partisan music preferences, including how political endorsements by musical artists might influence individuals’ listening habits, and
the potential ordering effect of asking respondents to evaluate their own music preferences before considering broader partisan music preferences, or vice versa.
Expectations
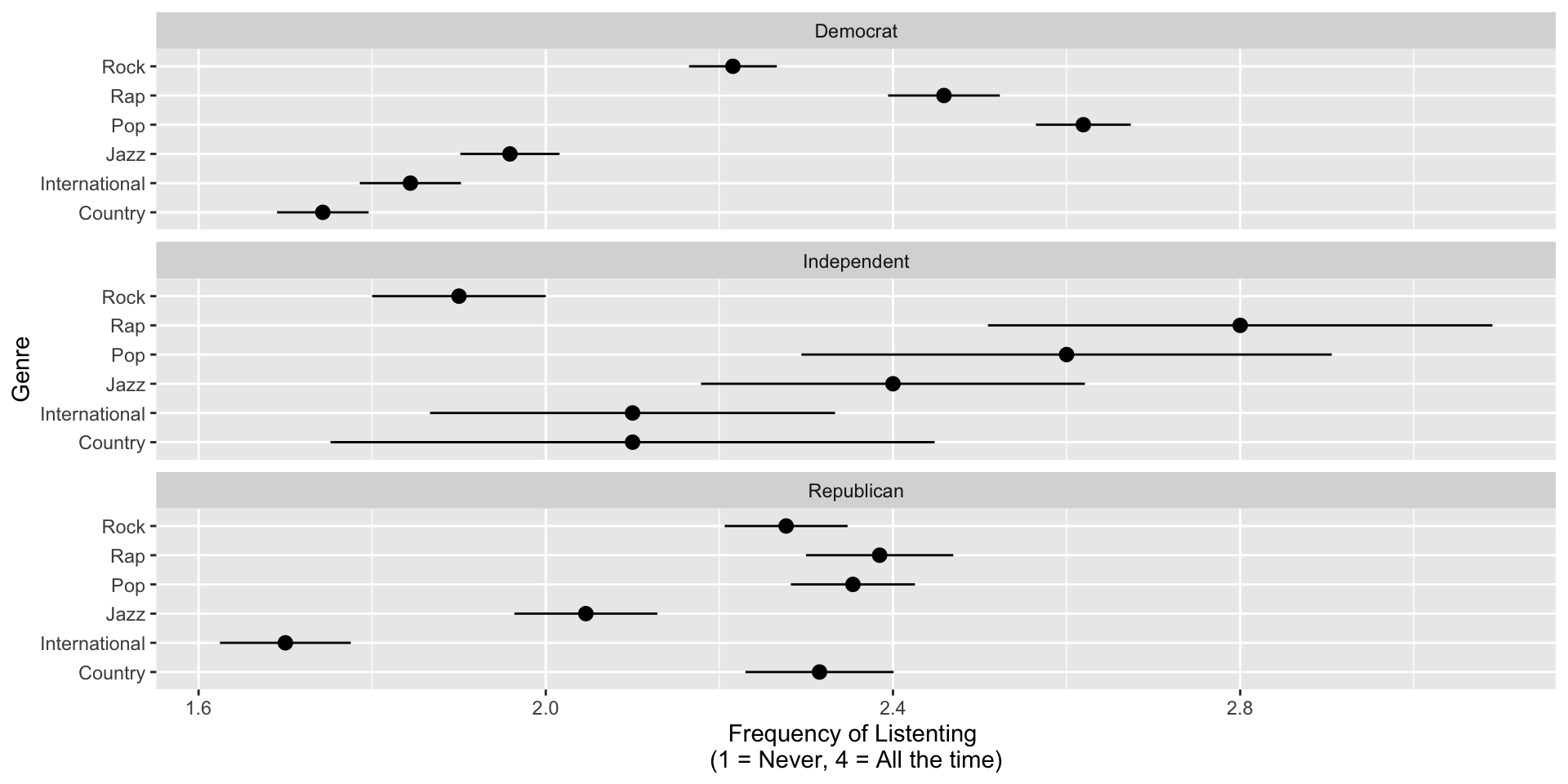
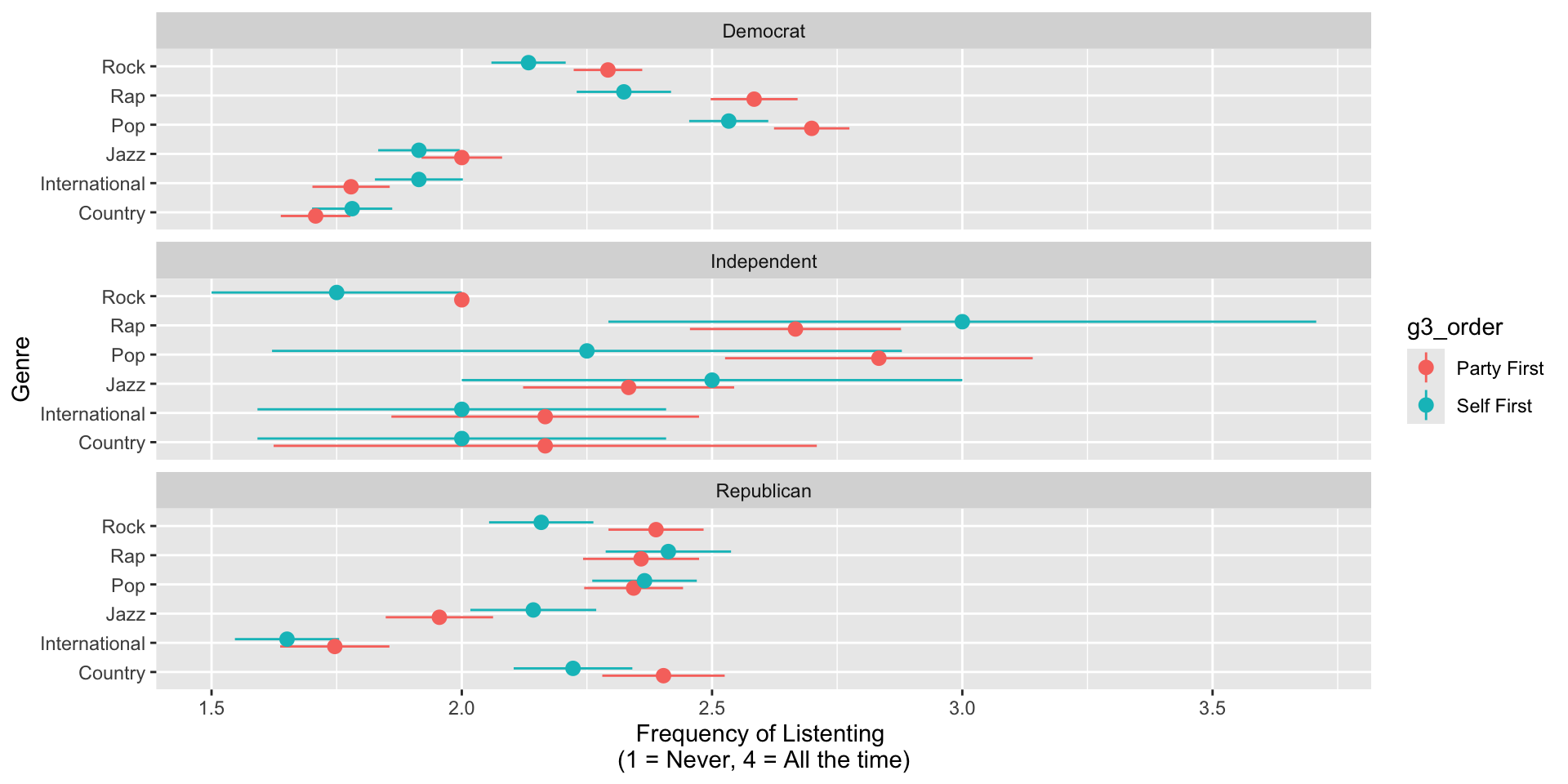
H1: We expect respondents who begin with the partisan music preference questions may report greater sensitivity to political endorsements, such as being less likely to listen to music associated with opposite-party endorsements, as the partisan framing could heighten their political identity.
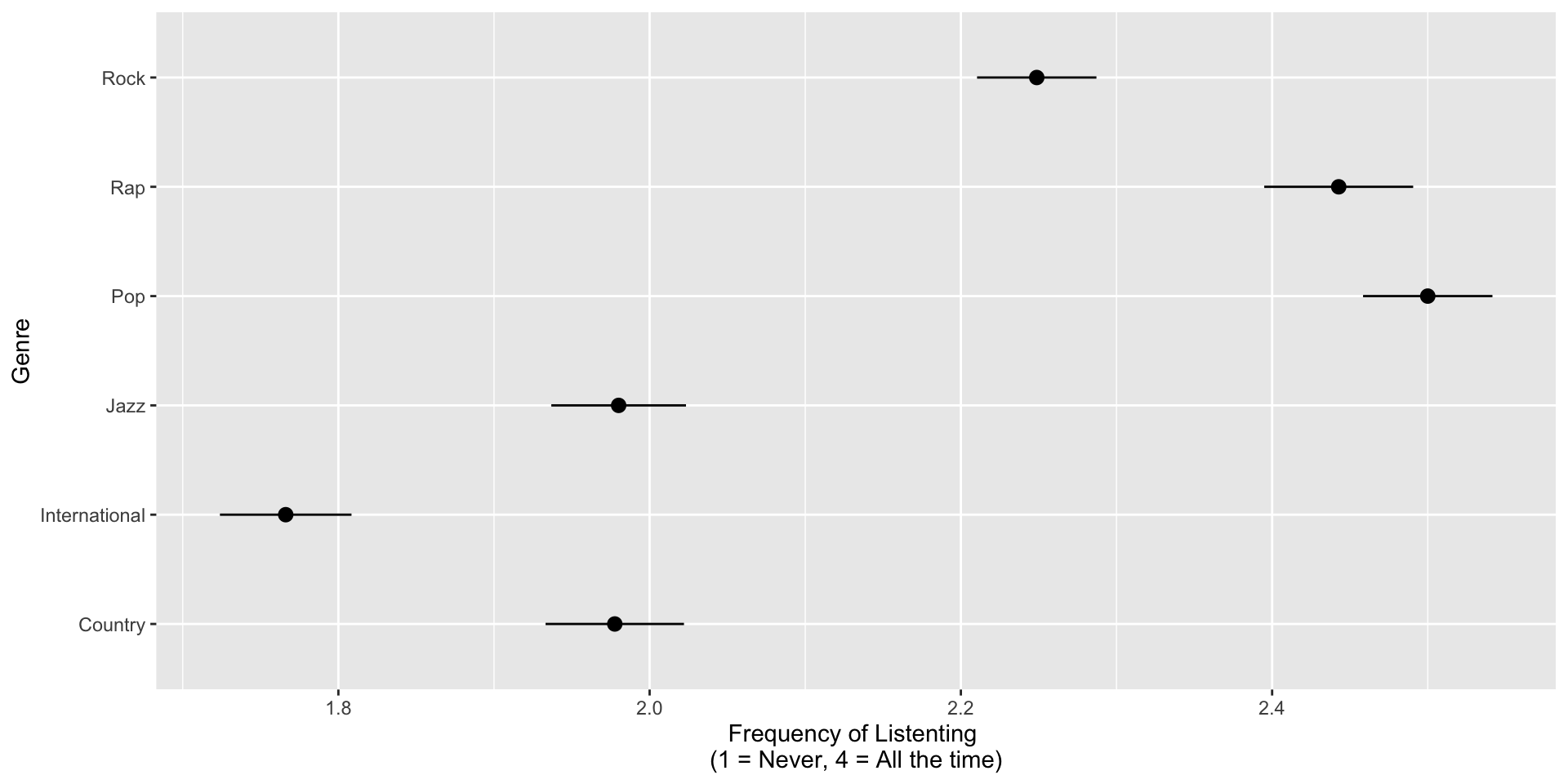
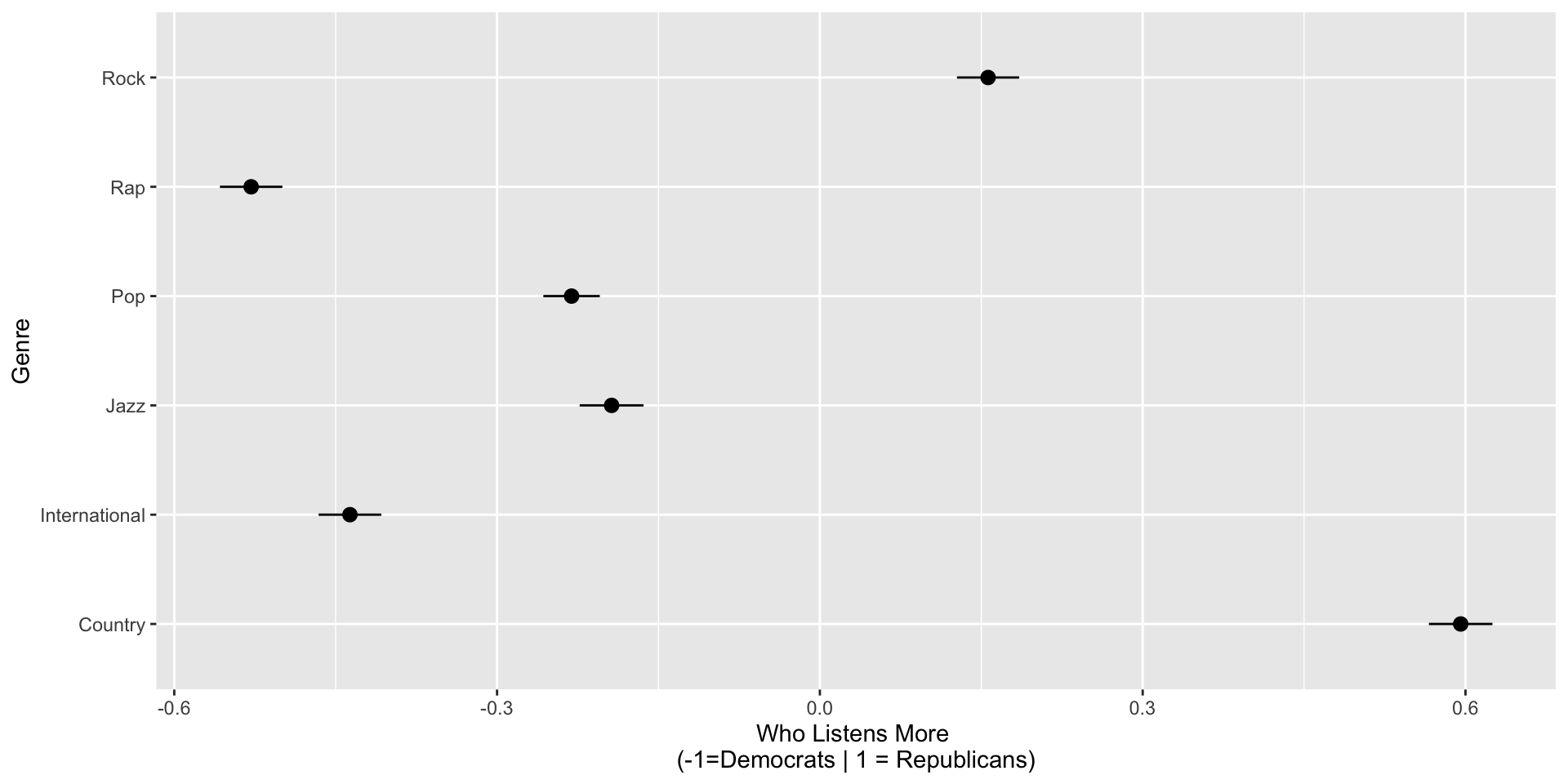
H2: We expect respondents will rate genres like rap/hip-hop, jazz/classical, international (foreign), and pop as more Democratic. Conversely, we expect respondents will rate country and classic rock as more Republican.
Listening Preferences
Listening Preferences by Partisanship
Listening Preferences by Partisanship and Order
Perceived Partisanship of Genre’s Listeners
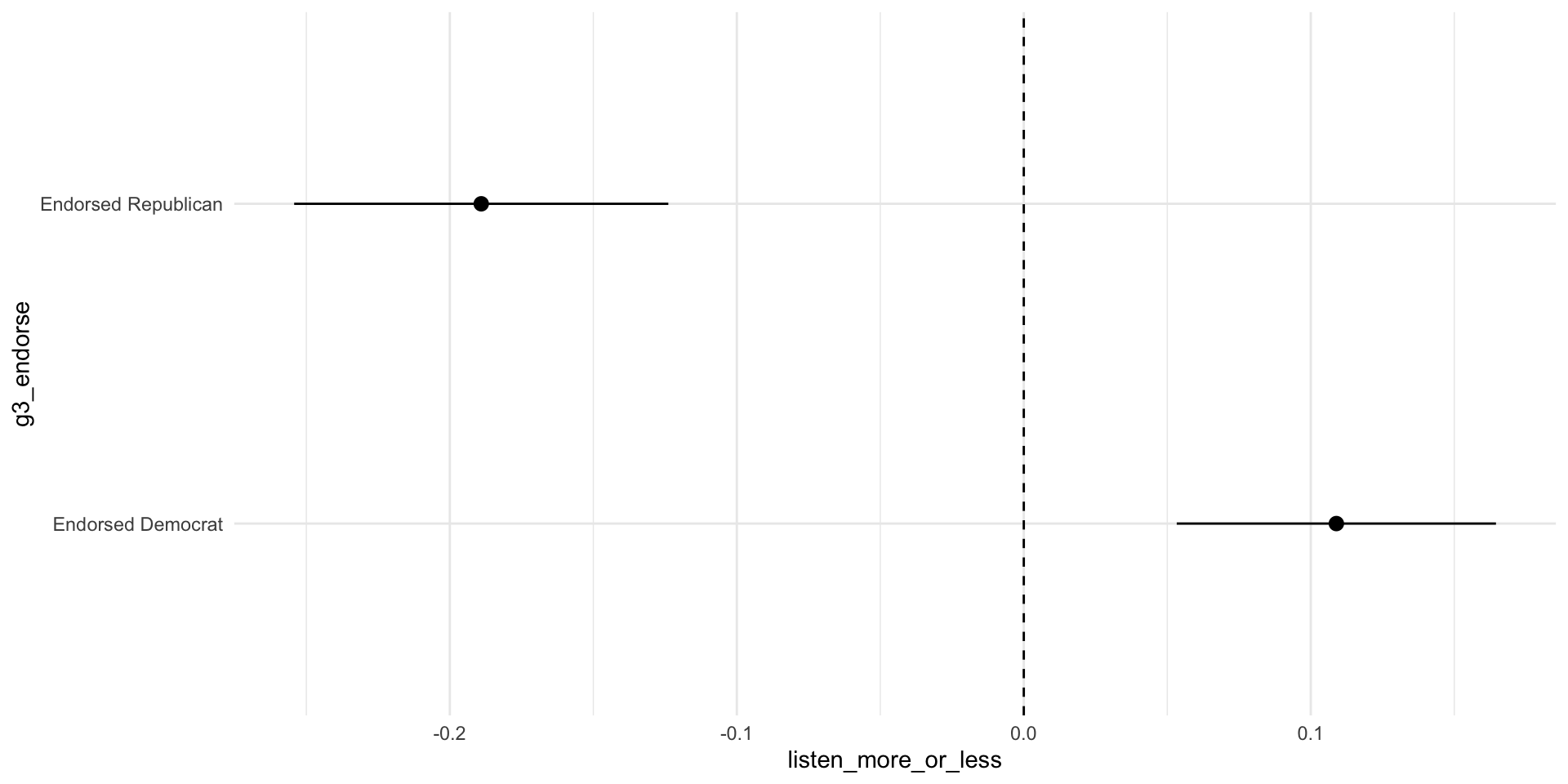
What if favorite musician endorsed: Democrat/Republican
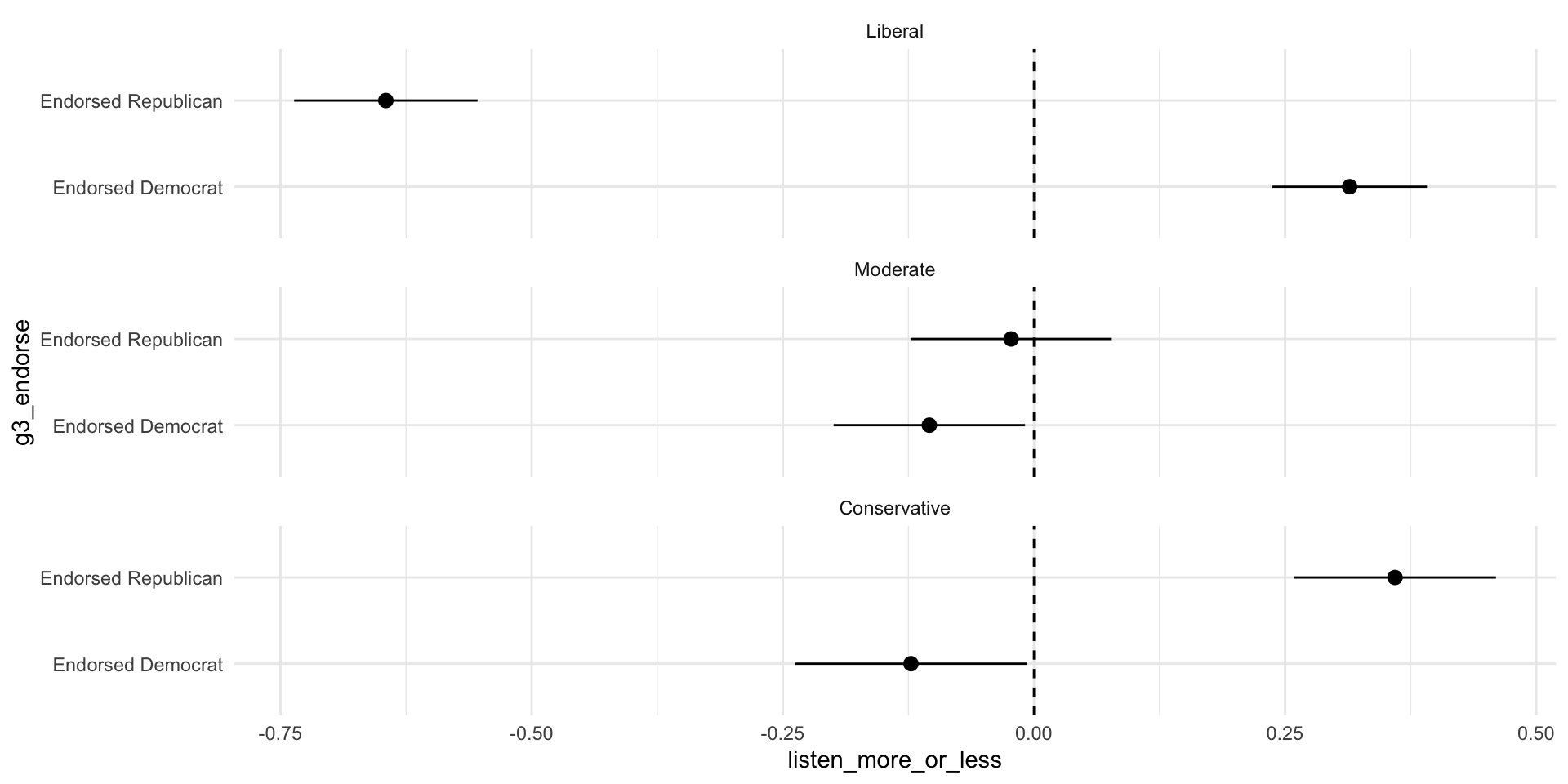
By ideolgoy
Group 4
Anastasios Demopoulos, Mikael Oberlin, Joshua Silverman
Project
We are interested in understanding
how different demographic groups respond to media coverage of voter suppression policies, and
how does being a member of an underrepresented minority group (URM) correlate with trust or distrust in mainstream media?
Expectations
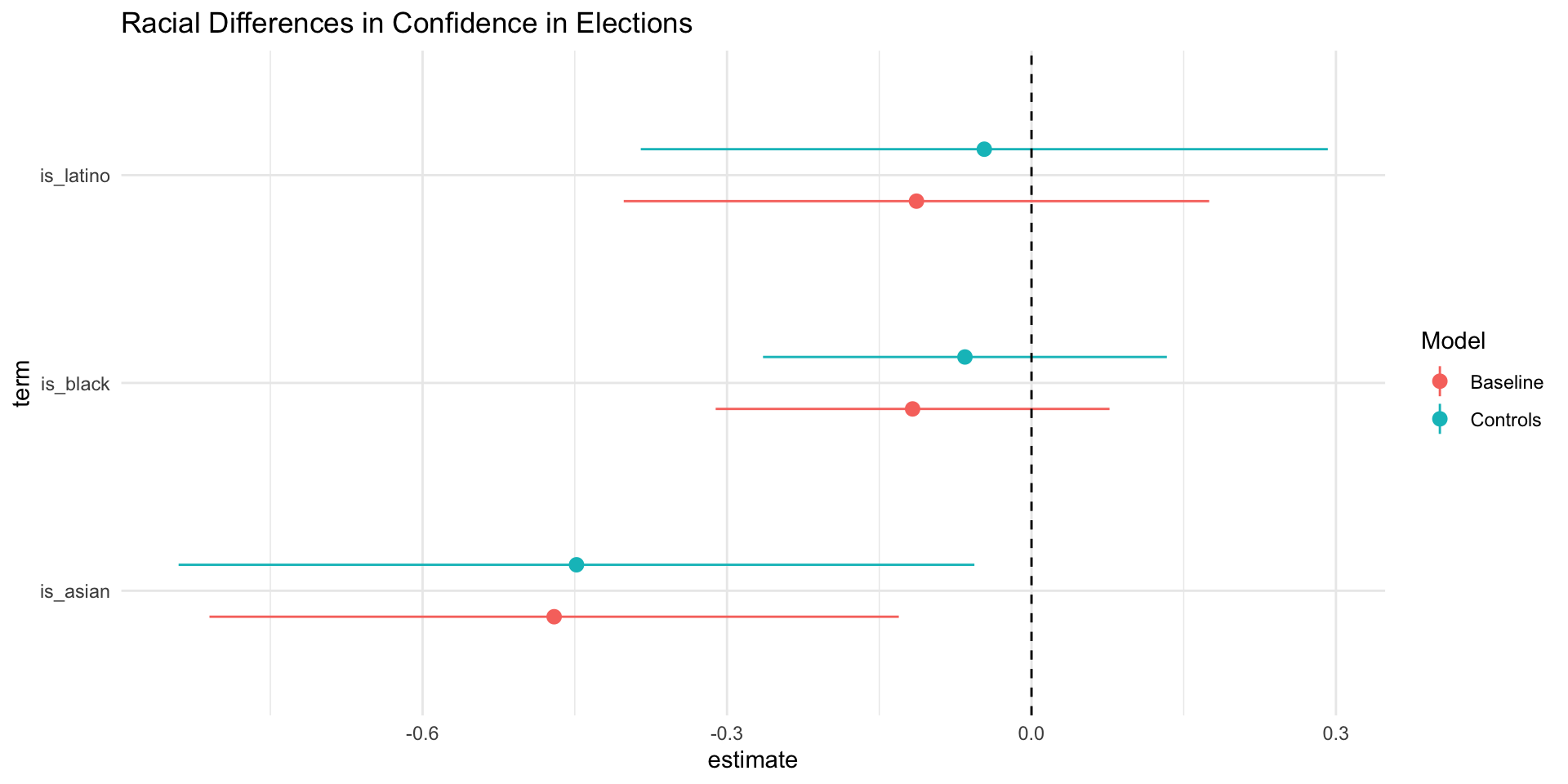
Confidence in Elections by Race
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 3.13*** | 2.65*** |
| (0.05) | (0.17) | |
| is_black | -0.12 | -0.07 |
| (0.10) | (0.10) | |
| is_asian | -0.47** | -0.45* |
| (0.17) | (0.20) | |
| is_latino | -0.11 | -0.05 |
| (0.15) | (0.17) | |
| is_rep | 0.12 | |
| (0.09) | ||
| is_ind | -0.58* | |
| (0.25) | ||
| age | 0.00 | |
| (0.00) | ||
| is_woman | -0.19* | |
| (0.09) | ||
| has_ba | 0.13 | |
| (0.10) | ||
| income | 0.10** | |
| (0.03) | ||
| R2 | 0.02 | 0.12 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.02 | 0.10 |
| Num. obs. | 403 | 352 |
| RMSE | 0.82 | 0.80 |
| ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05 | ||
Coefficient plots
Group 5
Bridget Hickton, Sailihe Men, Riya Srinivasan, Jack Zarate
Project
We are interested in how public opinion of celebrities changes when they endorse politicians and how public opinion of these endorsements varies across different levels of age, education, and political ideology.
Expectations
H1: We expect that public opinion of celebrities will be more extreme when the politician they endorsed is given
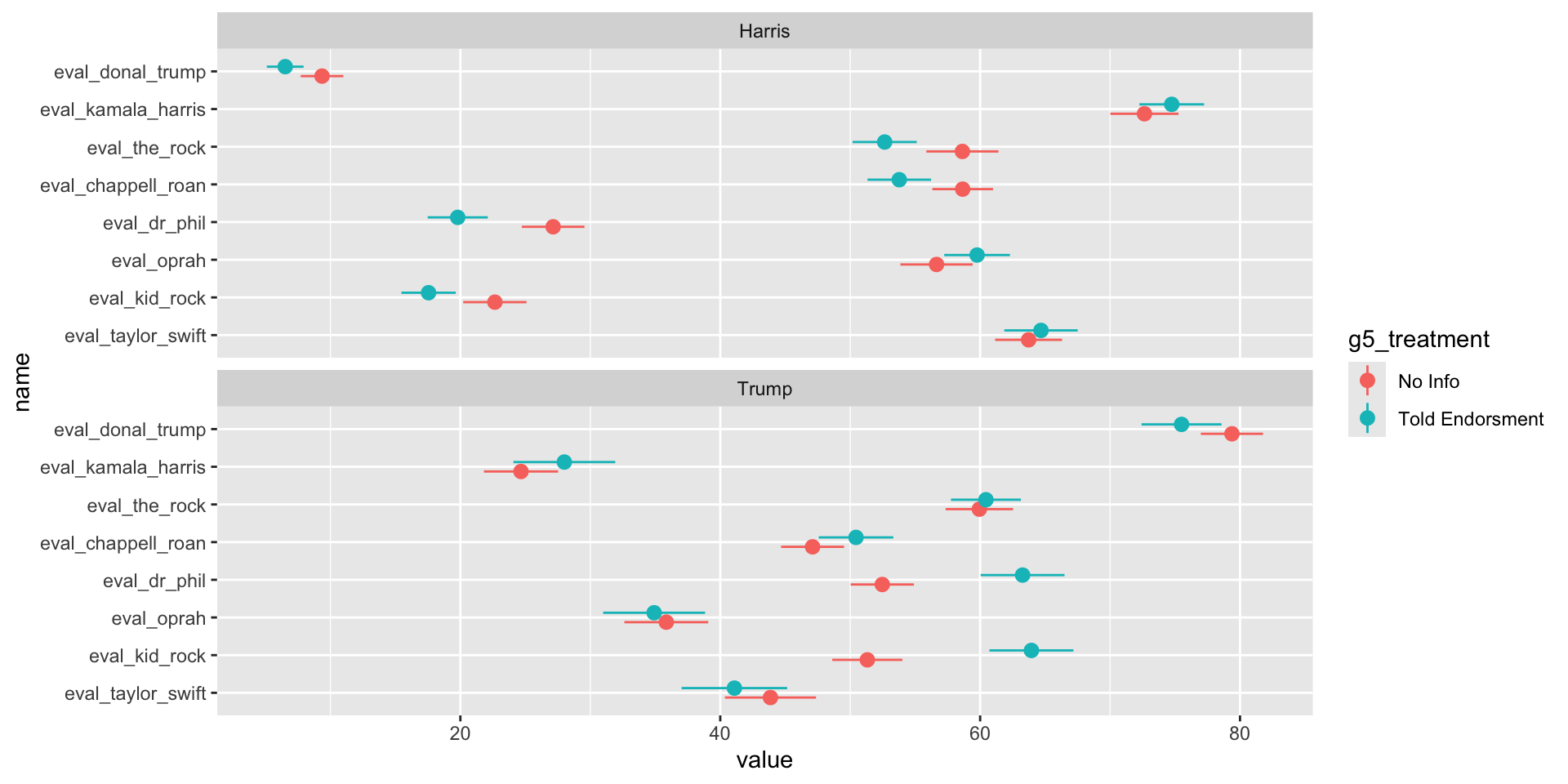
H2: Favorability toward a celebrity is positively associated with the likelihood of voting for the politician they endorsed.
Knowledge of Celebrity Endorsements
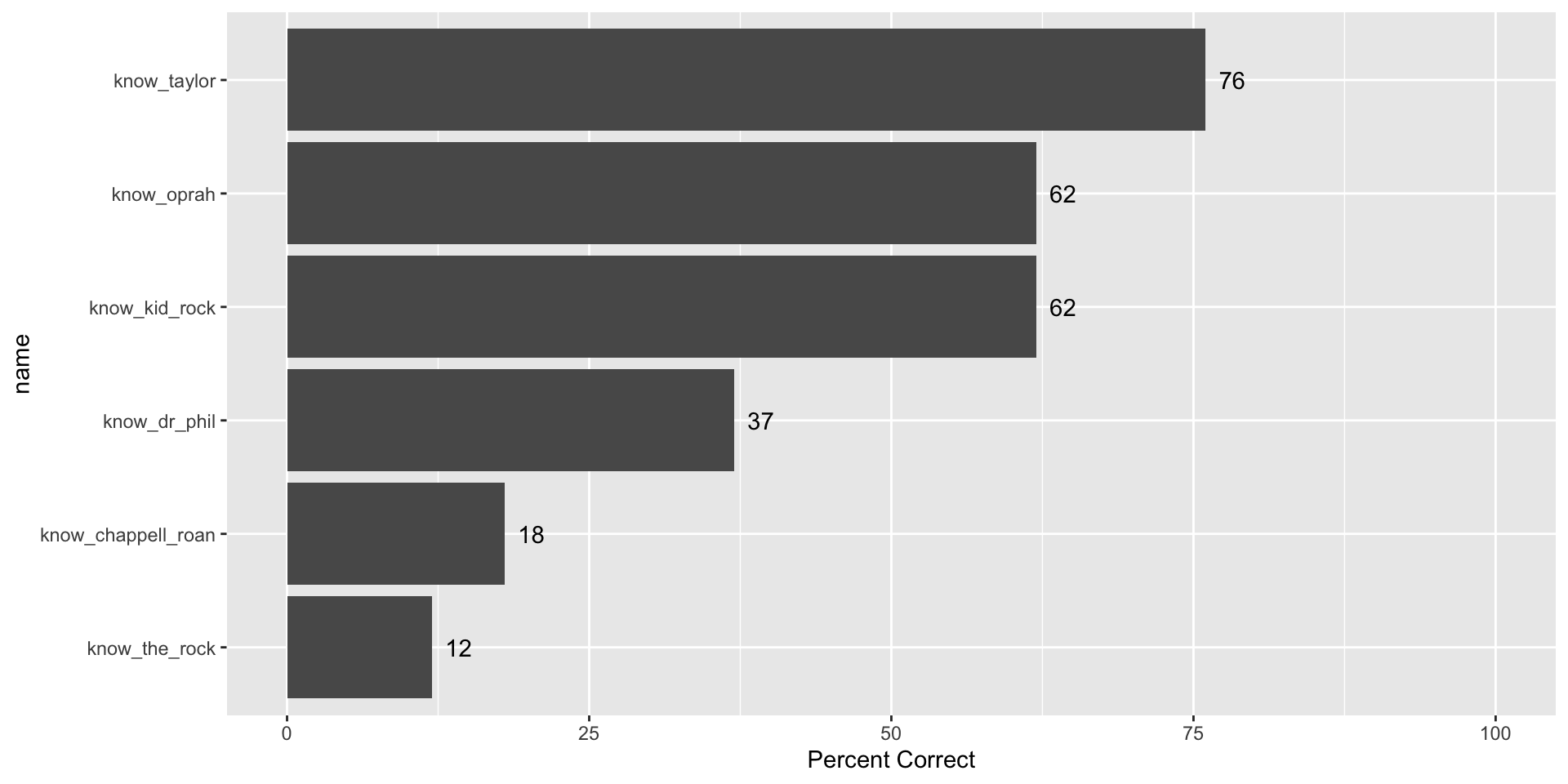
Impact of Knowing Celebrity Endorsments
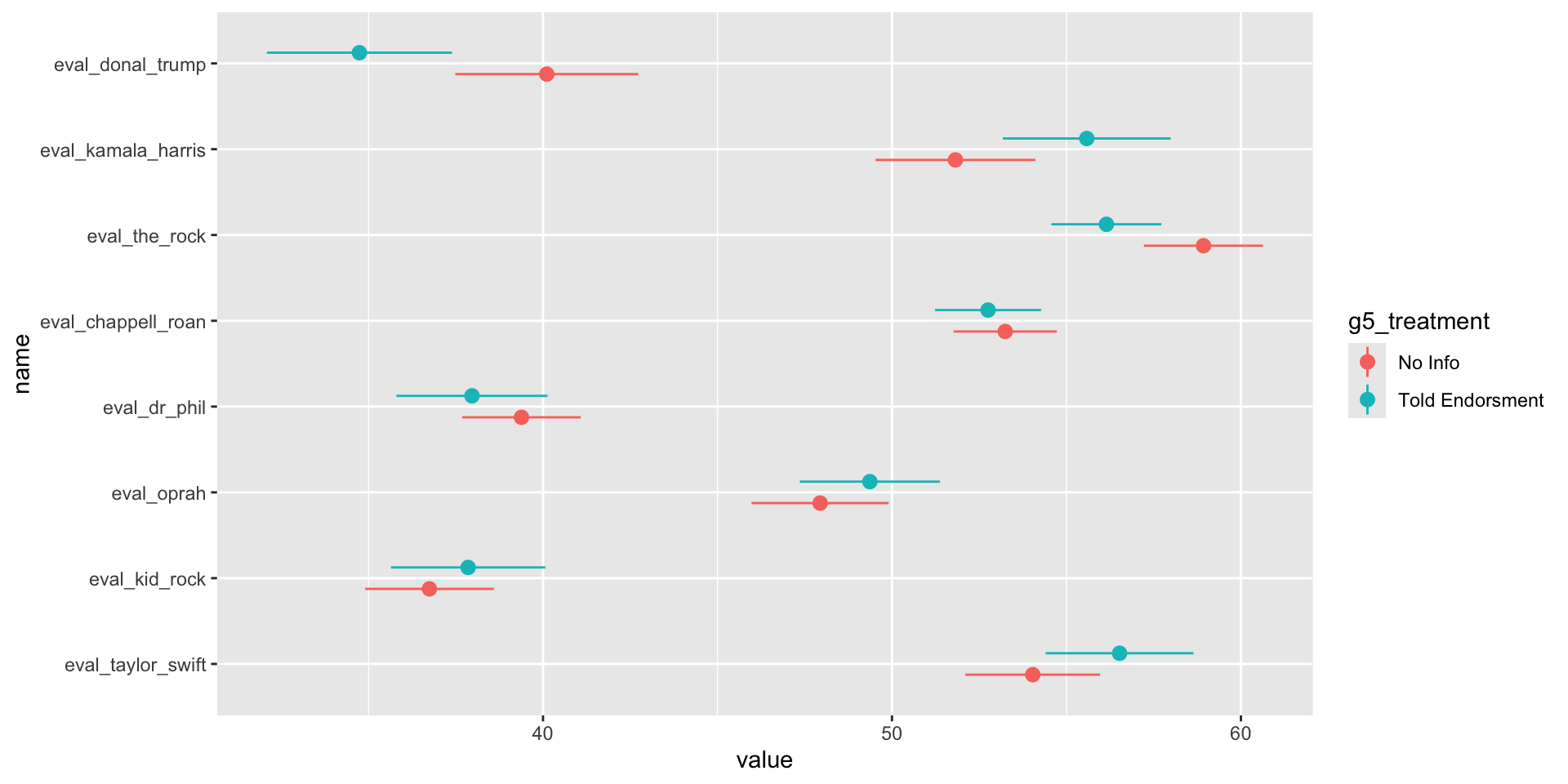
Impact of Knowing Celebrity Endorsments by Vote Choice
Group 6
Patrick Behan, Brandon Bergner, Ellie Brault, Connor Swenson
Project
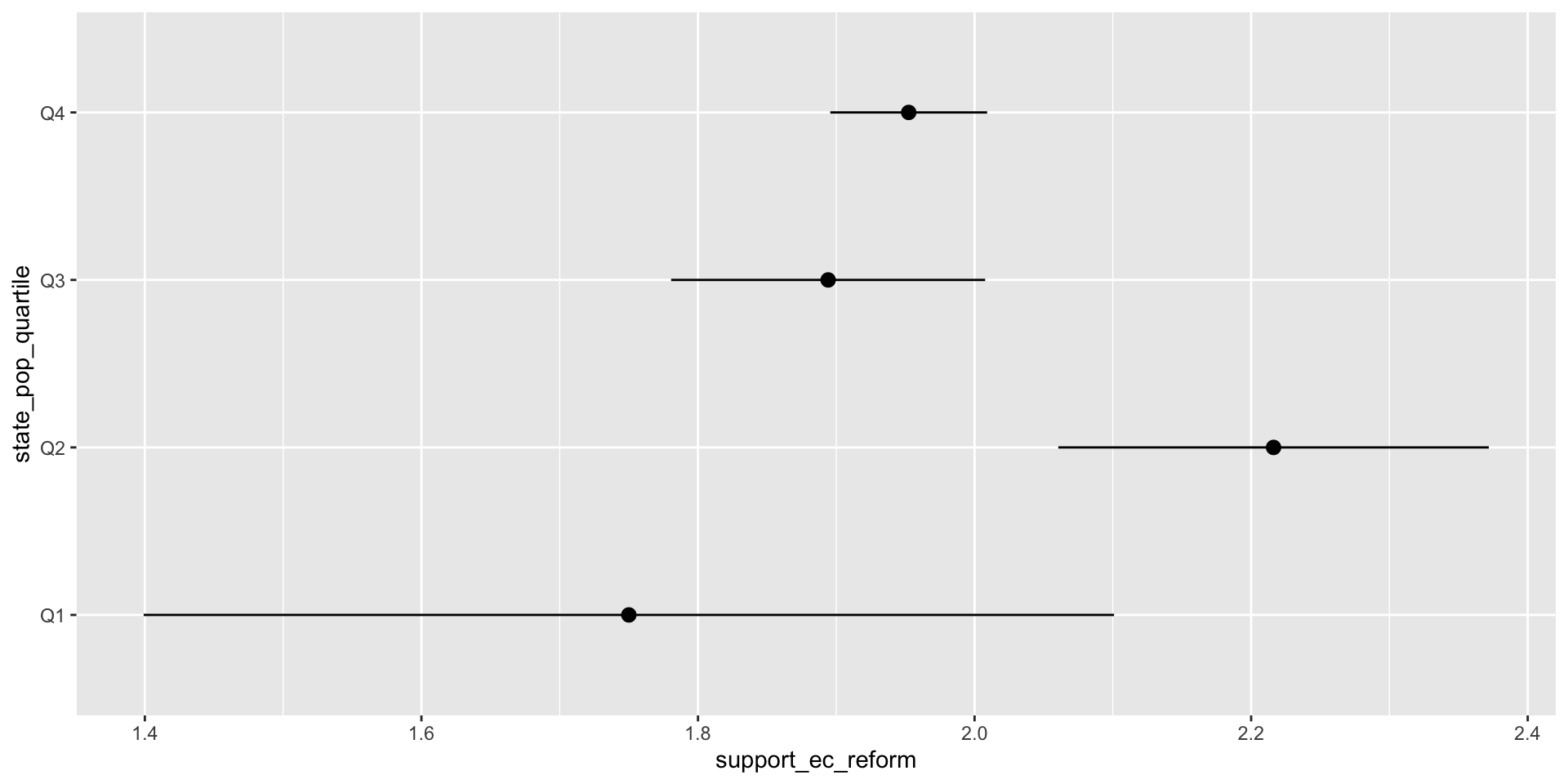
- We are interested in whether citizens from smaller states favor the Electoral College more than citizens from larger states.
Expectations
- We expect that citizens from smaller states favor the Electoral College more than citizens from larger states.
Data
library(zipcodeR)
library(tidycensus)
# Get State and County from Zipcode
df$state <- NA
df$county <- NA
for(i in 1:403){
df$state[i] <- try(reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i])$state)
df$county[i] <- try(reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i])$county)
}Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0
Error in reverse_zipcode(df$zipcode[i]) :
Invalid ZIP code detected, expected 5 digit ZIP code, got 0df %>%
mutate(
state = ifelse(nchar(state)>2, NA, state),
county = ifelse(grepl("(zip_char != 5)", county), NA, county)
) -> df
# Load county fips data, merge in df
data("fips_codes")
df <- df %>% left_join(fips_codes, by=c("county"="county", "state" = "state" ))
df %>%
mutate(
fips = paste(state_code, county_code, sep="")
) -> df
# Load ACS Data
state_pop <- get_acs(
geography = "state",
variables = "B01003_001",
year = 2020
)
state_pop %>%
mutate(
state_code = GEOID,
state_population = estimate
) -> state_pop
# Merge state population
df <- df %>% left_join(state_pop)
# County Data
county_pop <- get_acs(
geography = "county",
variables = c("B01003_001", "B01001B_001"),
output = "wide",
year = 2020
)
county_pop %>%
mutate(
county = NAME,
fips = GEOID,
county_population = B01003_001E,
county_black = B01001B_001E,
per_black_county = county_black/county_population
) -> county_pop
df <- df %>% left_join(county_pop %>%
select(fips, per_black_county, county_population,county_black ))
# Recode Group 6 Variables
df %>%
mutate(
support_ec_reform = g6_ec_reform - 4,
state_pop_quartile = case_when(
state_population <= quantile(state_pop$state_population)[2] ~ "Q1",
state_population > quantile(state_pop$state_population)[2] &
state_population < quantile(state_pop$state_population)[3] ~ "Q2",
state_population >
quantile(state_pop$state_population)[3] &
state_population < quantile(state_pop$state_population)[4] ~ "Q3",
state_population >
quantile(state_pop$state_population)[4] ~ "Q4"
),
from_big_state = ifelse(state_population > quantile(state_pop$state_population)[4],1,0)
) -> df
df %>%
ggplot(aes(state_pop_quartile, support_ec_reform)) +
stat_summary() +
coord_flip()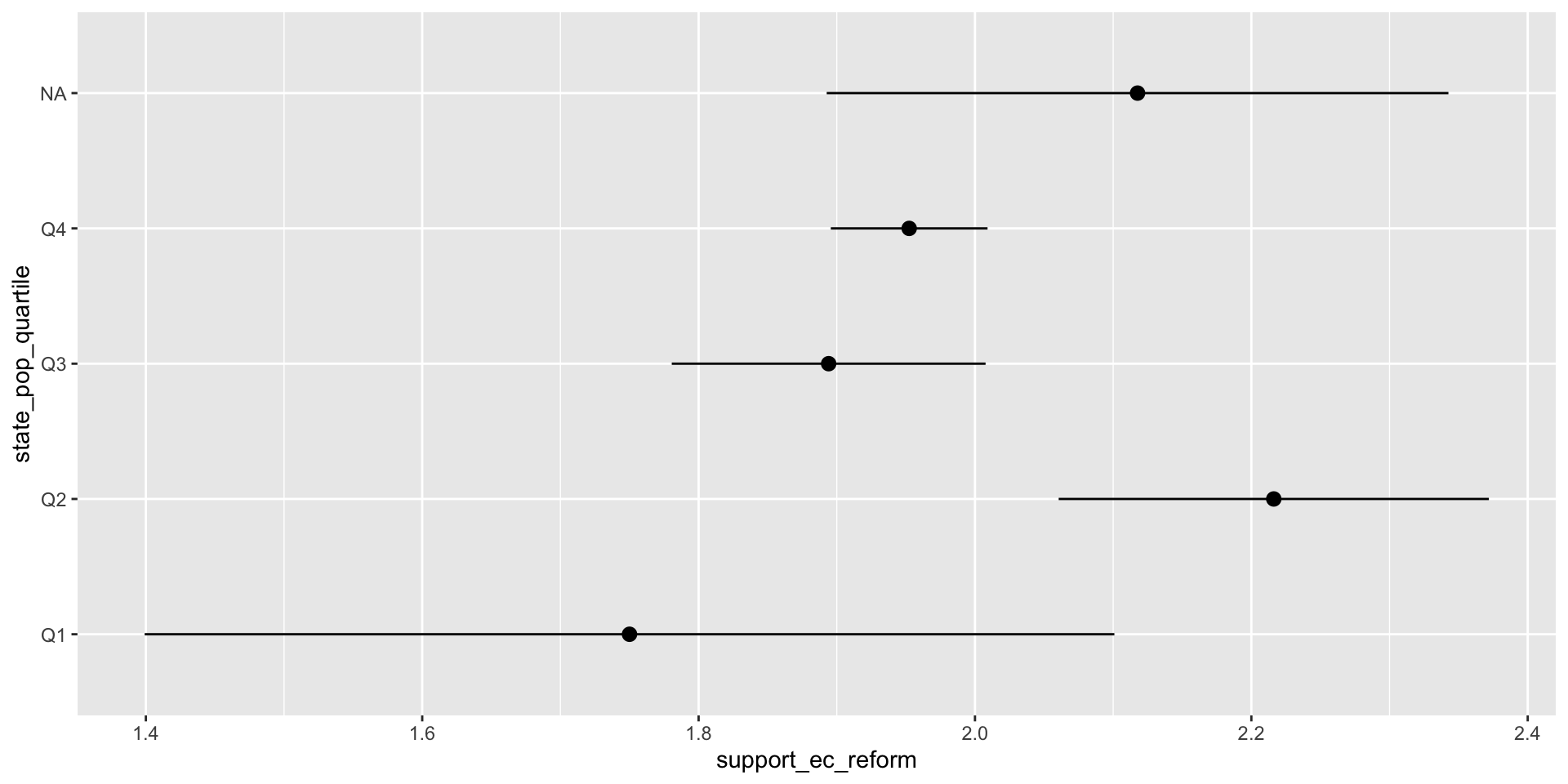
Respondents by Size
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
DC 1 0 0 0
ND 1 0 0 0
DE 2 0 0 0
ME 3 0 0 0
NH 2 0 0 0
HI 2 0 0 0
ID 1 0 0 0
WV 0 2 0 0
NE 0 1 0 0
NM 0 1 0 0
KS 0 2 0 0
MS 0 2 0 0
NV 0 5 0 0
UT 0 4 0 0
CT 0 5 0 0
OK 0 4 0 0
OR 0 11 0 0
KY 0 0 8 0
LA 0 0 3 0
AL 0 0 8 0
SC 0 0 7 0
MN 0 0 6 0
CO 0 0 6 0
WI 0 0 4 0
MD 0 0 4 0
MO 0 0 11 0
IN 0 0 8 0
TN 0 0 9 0
MA 0 0 3 0
AZ 0 0 8 0
WA 0 0 0 8
VA 0 0 0 12
NJ 0 0 0 8
MI 0 0 0 12
NC 0 0 0 11
GA 0 0 0 22
OH 0 0 0 8
IL 0 0 0 14
PA 0 0 0 19
NY 0 0 0 27
FL 0 0 0 29
TX 0 0 0 27
CA 0 0 0 55State Size and Support for EC Reform
Group 8
Tanner Burns, Serenity Hamilton, Charlie Jeffers, Christian Rasmussen
Project
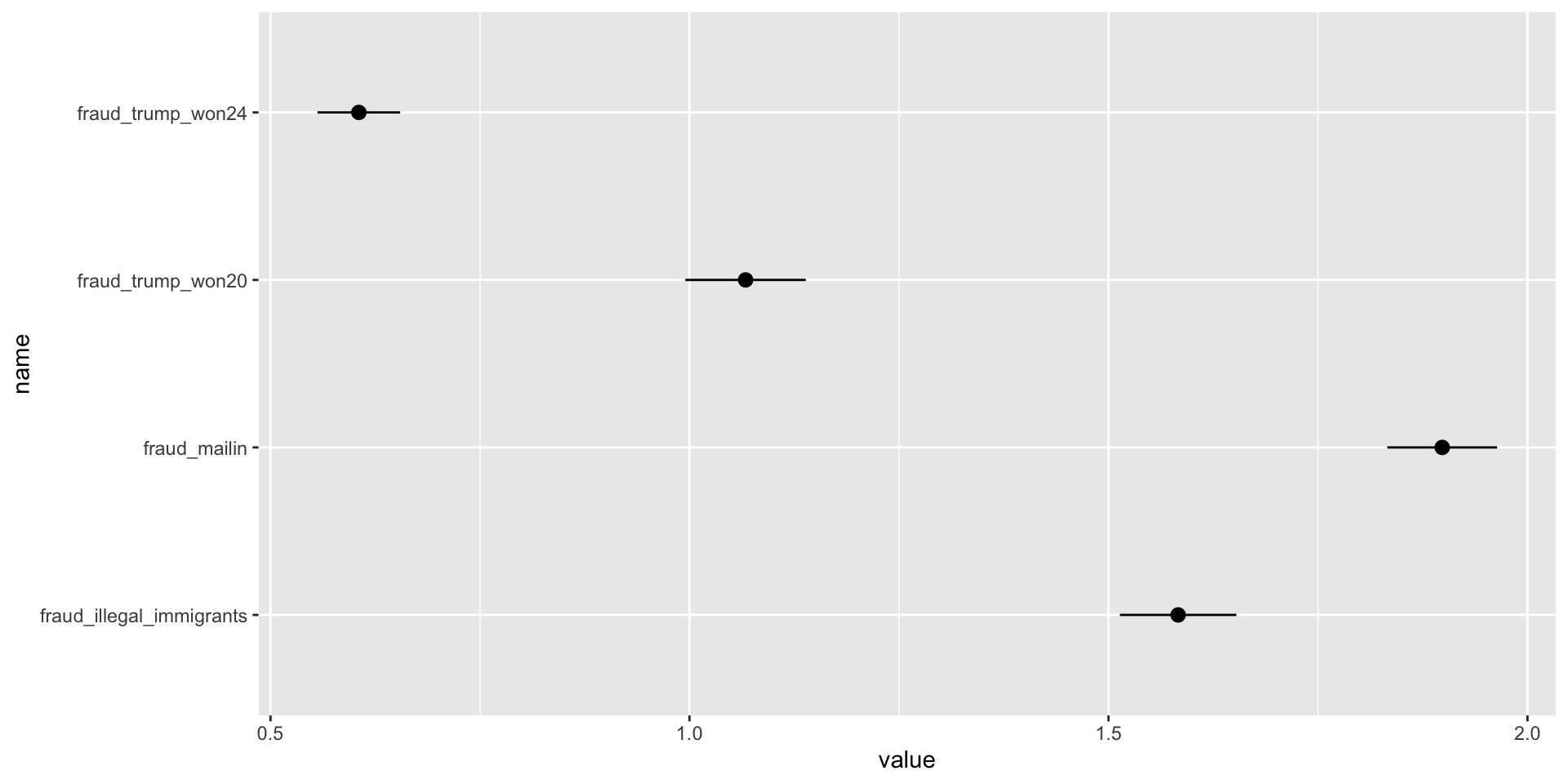
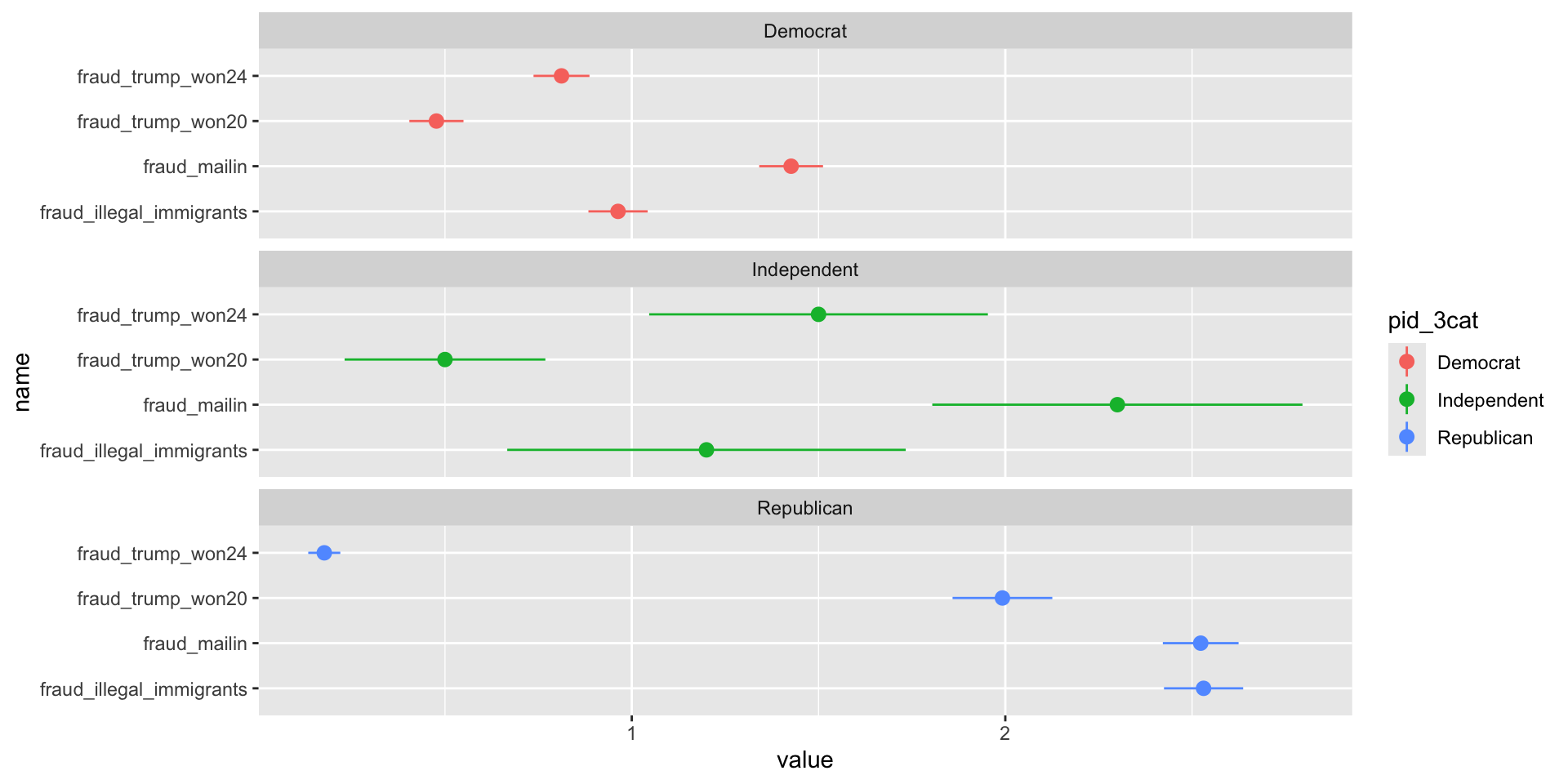
- We are interested in studying how certain beliefs about election denial are affected by voting decisions in the 2024 U.S. Presidential Election, and how political affiliation relates to the strength of the belief in election fraud
Expectations
H1: We expect that more moderate and liberal identifying people will display more confidence in the election process, while conservatives will have an increased belief in fraud. Non-voters may have higher belief in fraud as well.
H2: We expect that higher amounts of exposure to conservative media will be correlated with higher amounts of belief in fraudulent activity.
H3: We expect that respondents in younger age ranges will have a stronger relationship between media bias leaning and its influence on belief in the security and accuracy of elections.
Results
Fraud in Elections
Fraud in Elections by Partisanship
Group 9
Benjamin Buka, Maya Choksi, Kaicee Klus, Claire Mahoney
Project
We are interested in whether people actually align with the ideals of media sources affiliated with the party they identify with. To study this question, we want to present people with a short article containing the same information, but appearing to be from a left-leaning, neutral, or right-leaning source.
Expectations
H1: We expect that a person who identifies with a certain party is less likely to trust the information presented from a source that leans opposite from their own party.
H2: We expect that people may not full-heartedly agree with the information presented by a media source that skew towards their own political bias.
H3: We expect that independents will be less likely to trust any polarized media source, and will be more likely to align with the source with no lean.
Results
Biased of Article
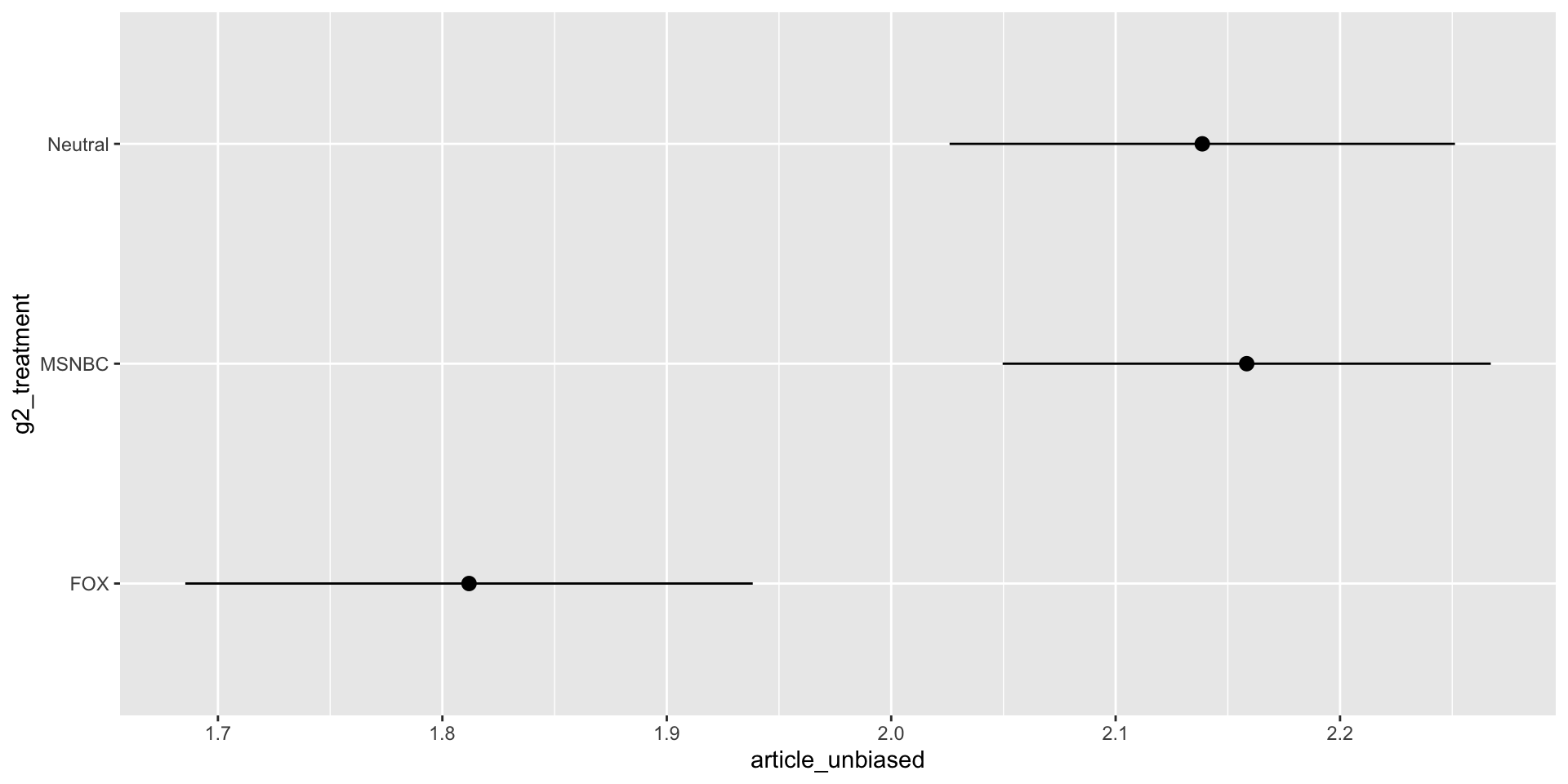
Biased of Article by Ideology
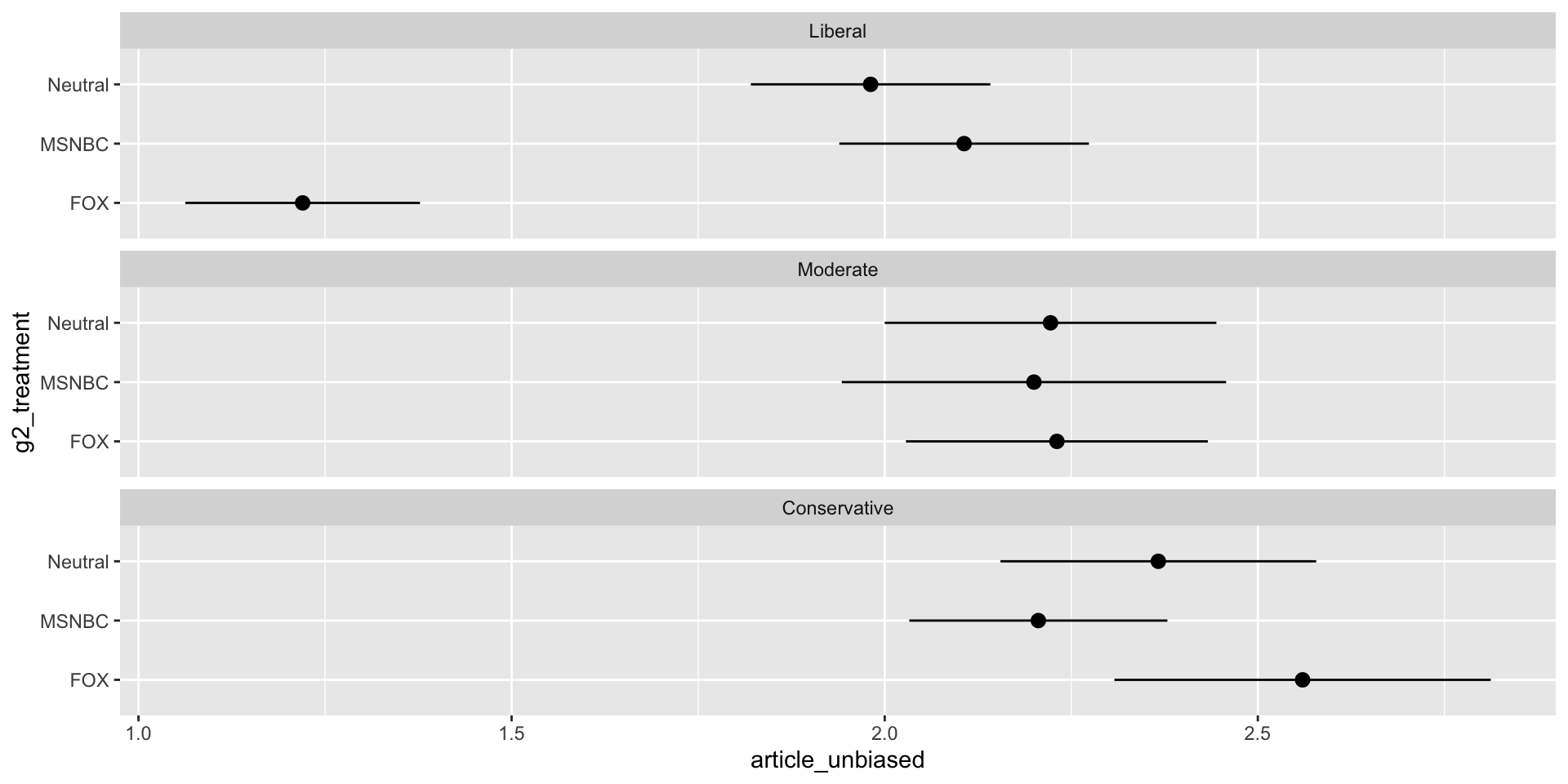
Useful Info
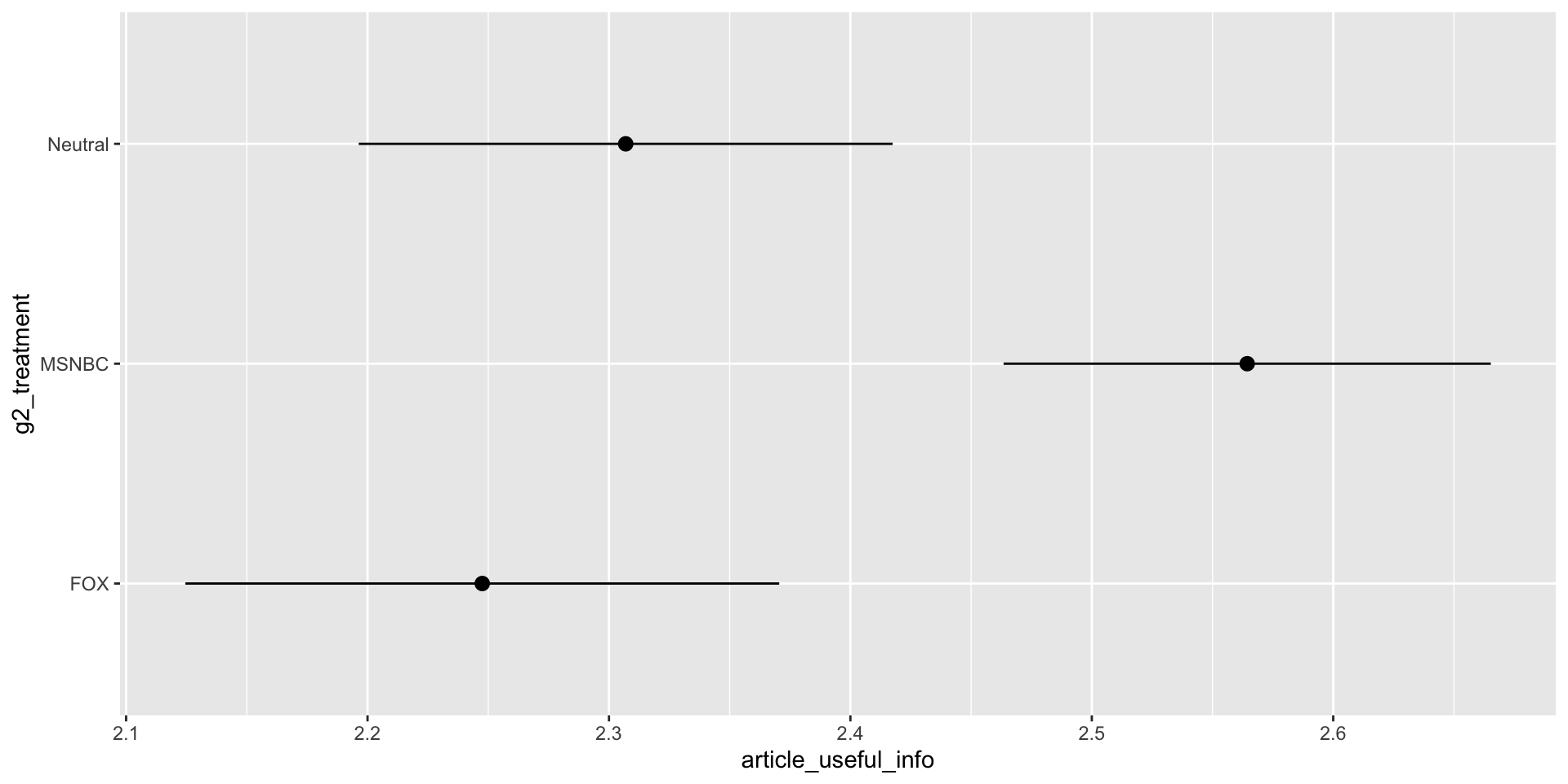
Useful Info by Ideology
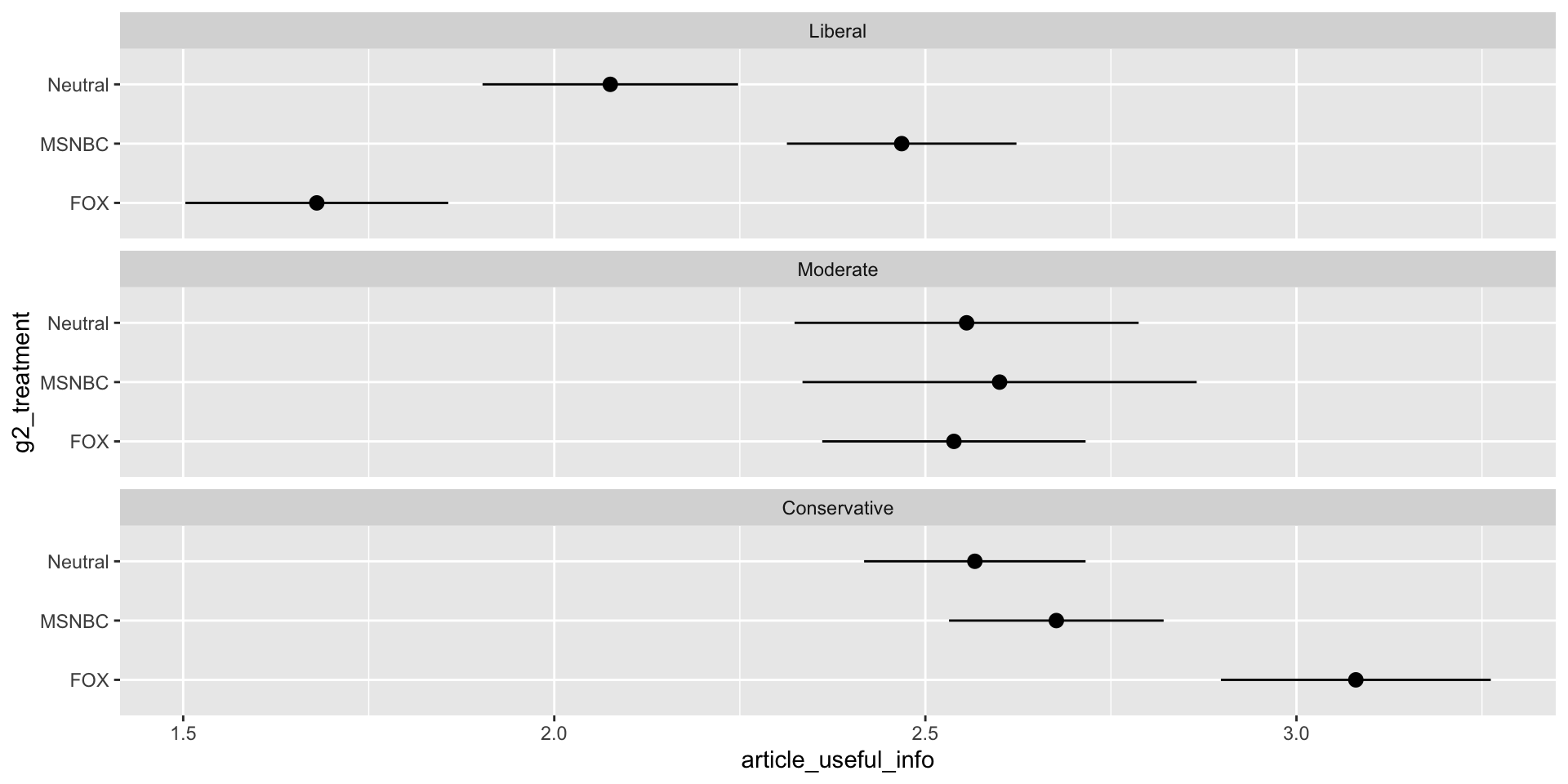
Increased Support
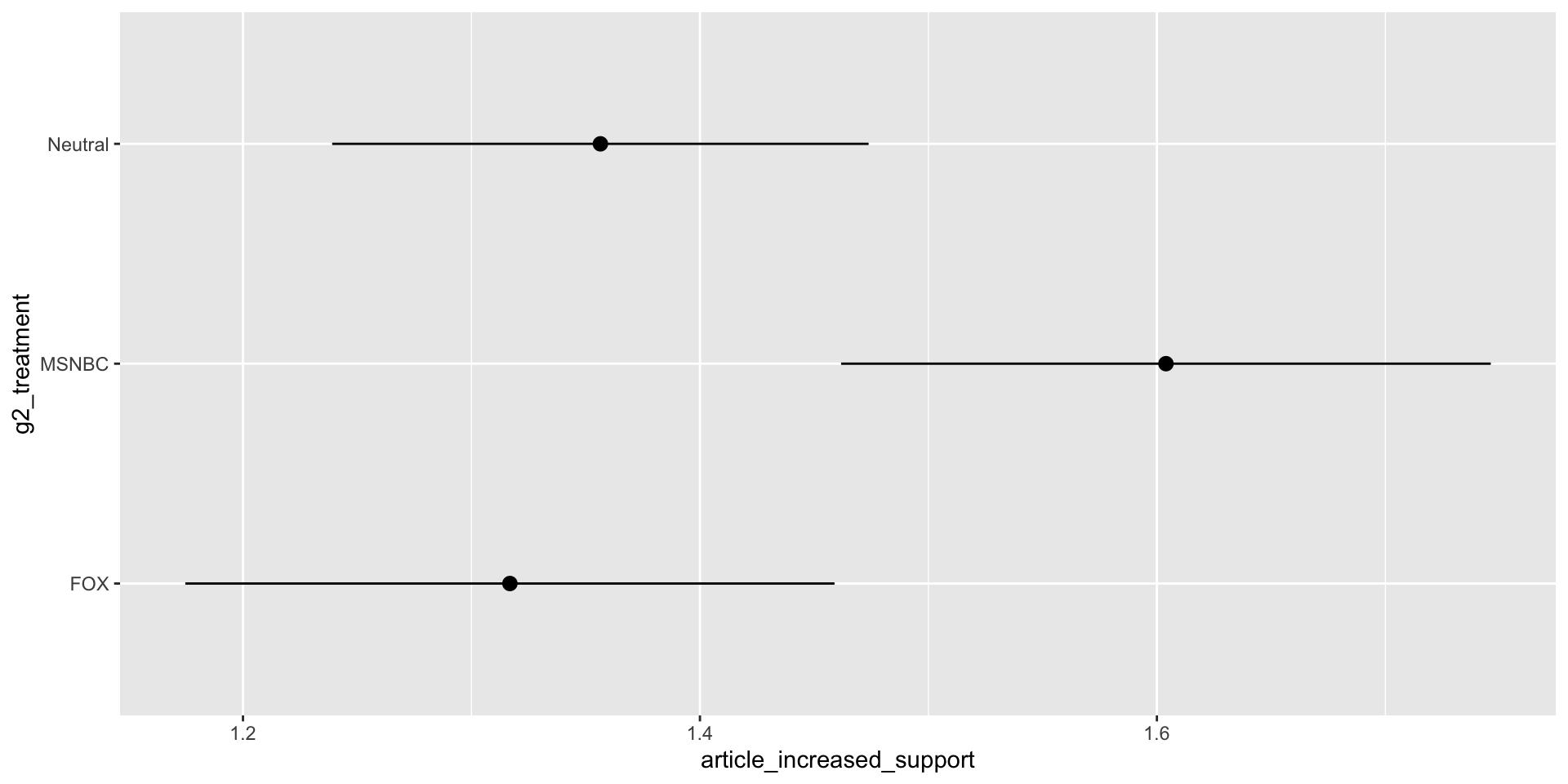
Increased Support by Ideology

POLS 1140